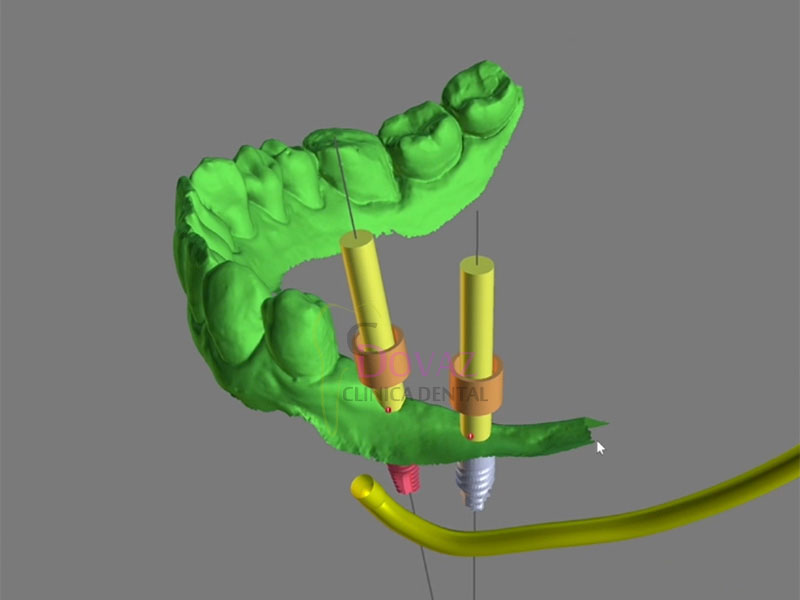
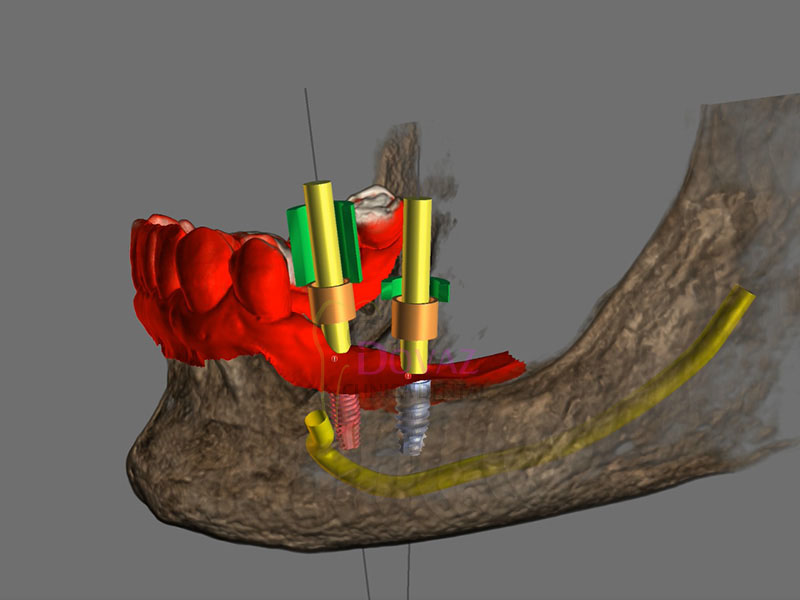
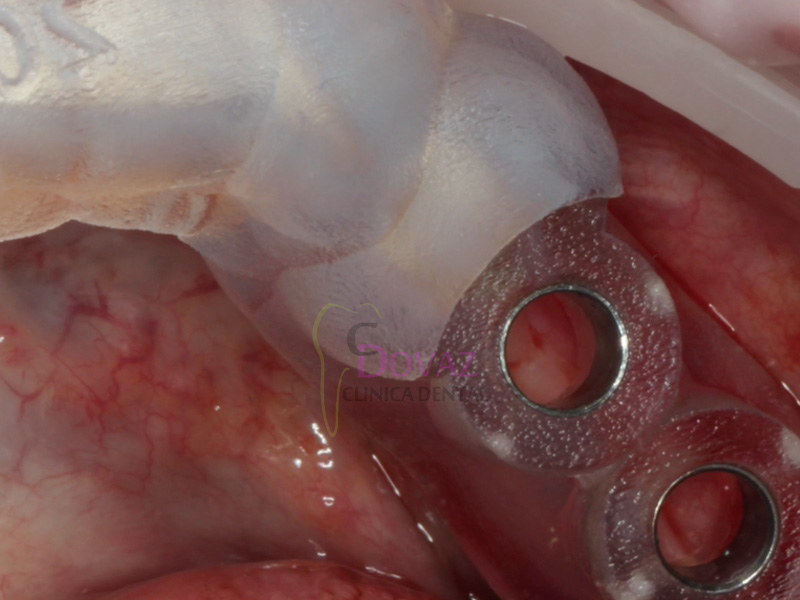
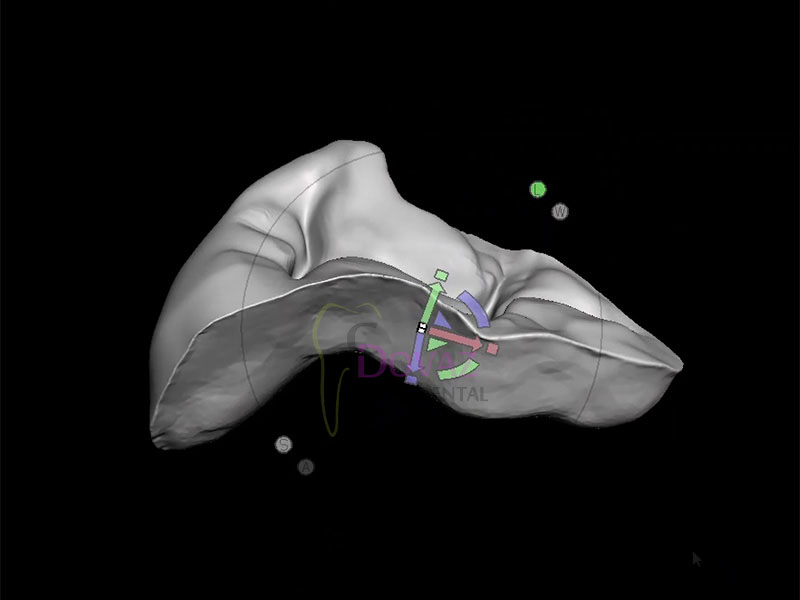
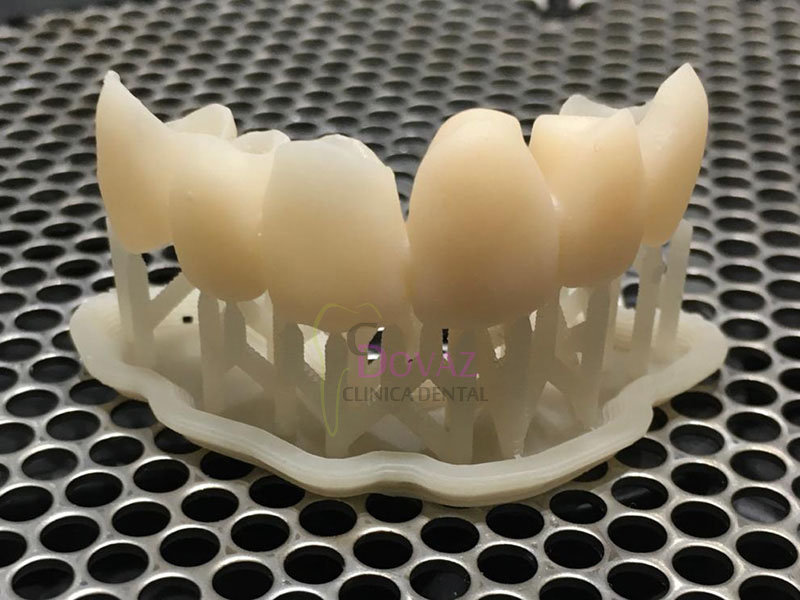
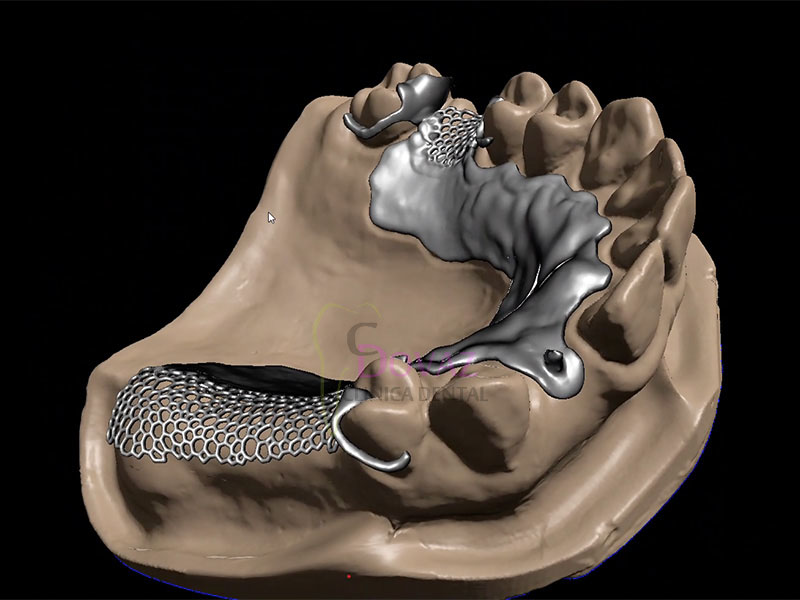
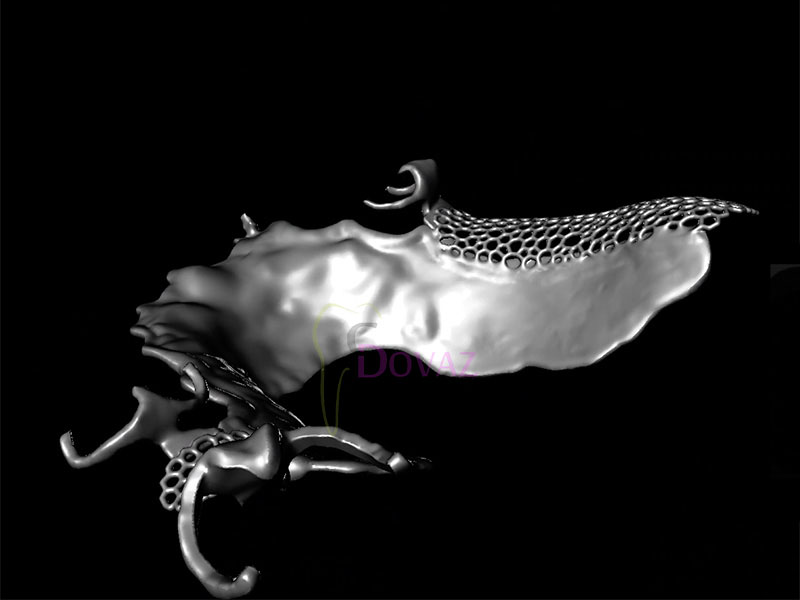
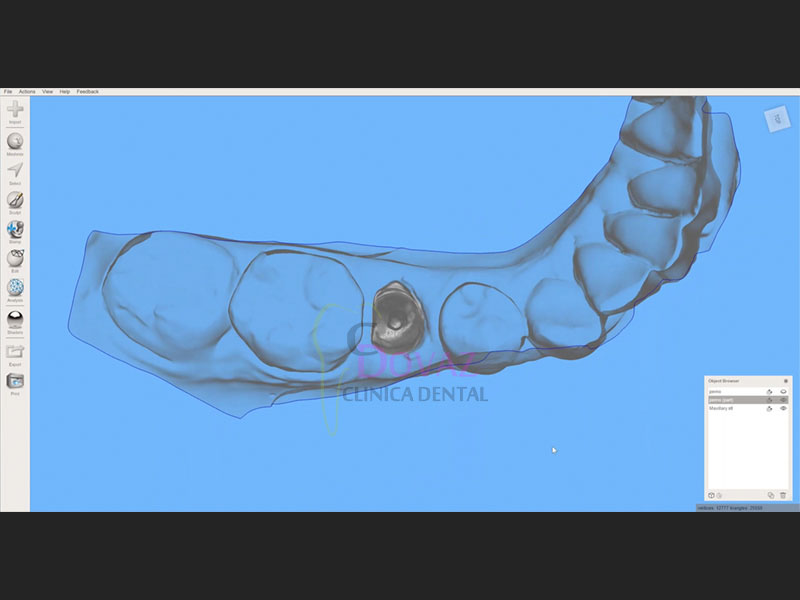
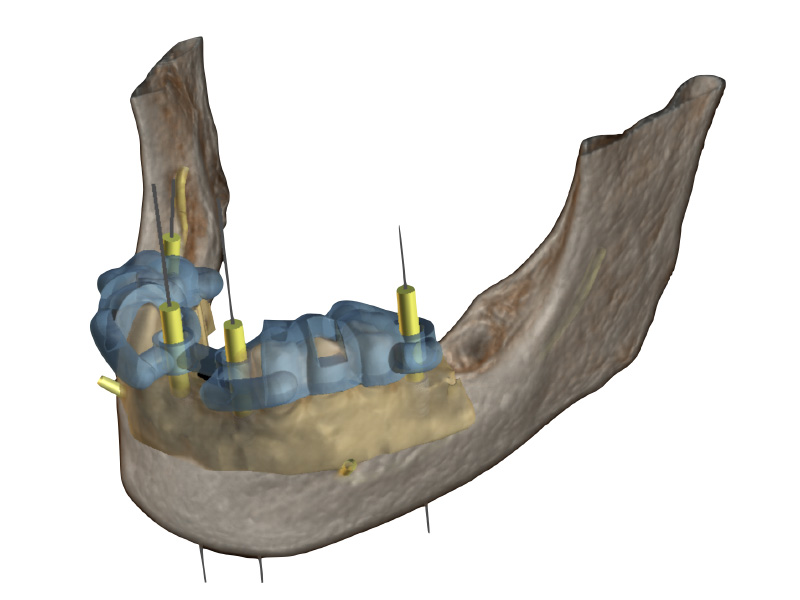
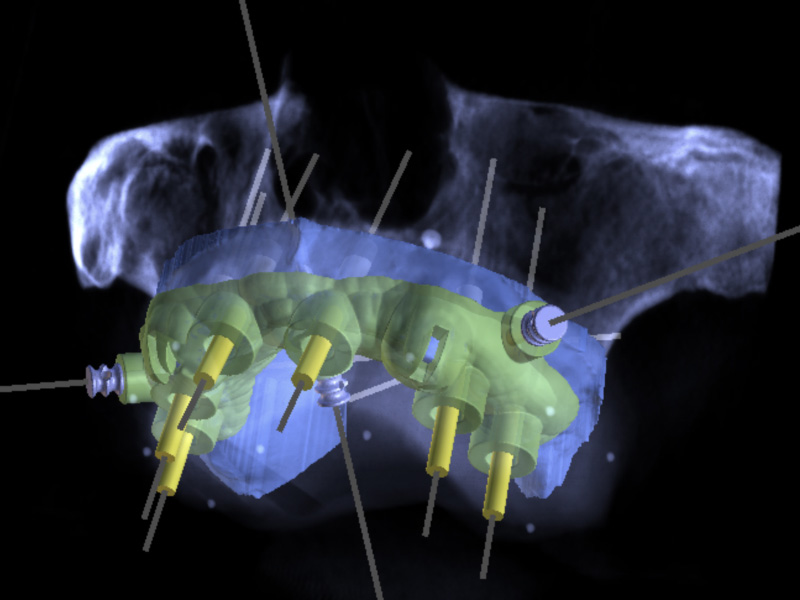
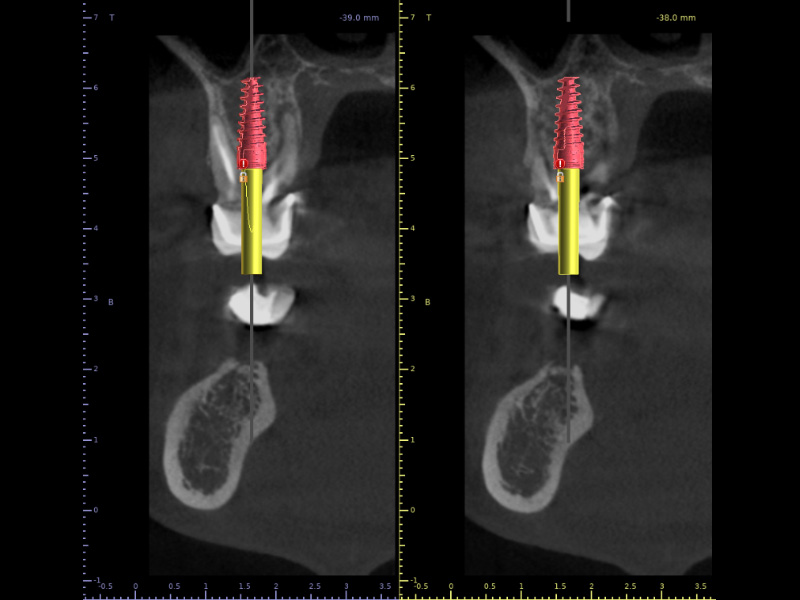
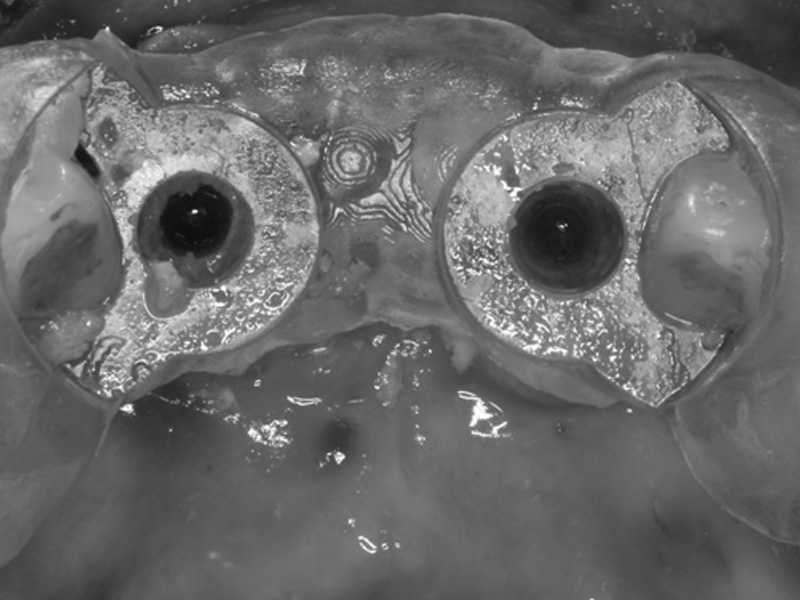
International Osteology Symposium. Barcelona. 27-29 Abril 2023.
Fecha: 27 al 29 de Abril de 2023
Lugar:
Centro de Convenciones Internacional de Barcelona
Plaza de Willy Brandt 11-14
08019 Barcelona
Visítanos!! Stand Claronav
y ven a probar el Navident 4 EVO

International Osteology Symposium
Solicita tu oferta durante el simposio, precios especiales...
No lo encontramos.
Mostbetcasino com Hesaba Giriş Yapamamak Ve Oyundan Atılma
Mostbetcasino com Hesaba Giriş Yapamamak Ve Oyundan Atılmak
MostBet En Güvenilir Casino Sitesi Slot sitesi
Content
- Mostbet Casino Hesaba Para Yatırma İşlemi Ve Destek Danışmanı Tarafından Engellendi
- Mostbet Giriş Güncel Adresi: Mostbet Giriş (mostbet Giriş)
- Sürdürülebilirlik Üretimde dünya standartlarında teknoloji, yüksek üretim kapasitesi ve temiz enerji.
- Mostbet Giriş Mostbet’e Hoş Geldiniz
- Mostbet Sitesine Vpn Ile Giriş Nasıl Sağlanır
- MostBet Yeni Giriş Üyeleri
- Mostbet Para Yatırma Seçenekleri Nelerdir? Para Yatırmak Güvenli mi?
- Admin, Mikro Medikal Kaynak Bayan Kuaförü Gökhan Sevim Sitesinin Yazarı Sayfa 25 33
- Türkiye’den oyuncular Mostbet’te oynamaya nasıl başlar
- Sweet Bonanza Slotunun Özellikleri
- Türkiye’de Mostbet’te bahis oynarken herhangi bir kısıtlama veya limit var mı?
- Mostbet – Türkiye’de Online Spor Bahisleri Şirketi
- Mostbet Türkiye: Resmi Site, Kayıt, Bonus 5 673 Giriş yapmak
- MostBet Güncel Giriş Canlı Tv Uygulaması
- Mostbet Türkiye On-line Giriş Yap Son Dakika Kocaeli Yaşam Haberleri
- Uygulamayı Neden Mostbet Yüklemelisiniz
- Mostbet Üye Ol
- Mostbet Giriş Türkiye Resmi Bahis Sitesine Ve On-line Kumarhaneye
- Mostbet Hakkında
- Мостбет Официальный Сайт Букмекерской Конторы Mostbet
- şikayetimi Belirttikten 30 Dakika Sonra Hesabıma Param Geldi Teşekkür Ederim
- Mostbet Hesabınıza Nasıl Giriş Yapılır?
- MostBet para yatırma ve çekme işlemleri
- Mostbet Türkiye Uygulaması Nasıl Indirilir?
- Mostbet bonusu hakkında
- Casino sitesi Mostbet canlı destek hattı
- Mostbet Casino Müşteri Hizmetleri İle Sorun Yaşıyorum
- Mostbet Trukiye Giris
- Betonred Canlı Casino — Turkish Casino Giriş ve Kayıt
- Mostbet çevrimiçi kumarhane
- MostBet Yeni Giriş Adresinde Yer Alan Bahis Hizmetleri
Bahis için sınırlı bir süre sağlanır, bu nedenle bahisçinin kazanç miktarını artırmak fırsatını kaçırmamak için acele etmesi önemlidir. Kullanılabilir diğer bir seçenek de cep telefonu iletişim numarası kullanarak kaydolmaktır. Spor bahislerinin tamamını meşhur ve güvenli altyapı sistemleri başarılı bir şekilde sunuyorlar. Yüksek oranlı bonusları bulunduğu için yatırım yapan ve bahisleri tutturan kullanıcılar daha çok kazanabilmektedir.
- Oyunda önemli olan, ayrıntılarını aşağıda ele alacağımız etkili stratejilerin seçimidir.
- Kombine bahislerinde kazanç bütün karşılaşma sonuçları oranının bahis miktarı ile çarpımına eşittir.
- Ayrıca etkinliğin gidişatını takip edebilir ve karşılaşmada eine olduğuna bağlı olarak oranların nasıl değiştiğini izleyebilirsiniz.
- Aviator Crash Game, her an çökebilecek bir büyüme eğrisinden oluşan yeni bir sosyal ve çok oyunculu oyundur.
Hoş Geldiniz Paketi, oyunları ve siteyi tanımanıza yardımcı olacak ve ayrıca Hoş Geldiniz Paketi sırasında 1.000€’ya kadar kazanacaksınız. Spor oyunlarından Star Trek’e kadar, geniş bir oyun yelpazesini tutmaya çalışıyoruz ve ardından bunları temalarına göre gruplandırıyoruz. Fransa, Hong Kong ve Malezya gibi diğer ülkeler, yalnızca kredi kartıyla ödeme kabul etmektedir.
Mostbet Casino Hesaba Para Yatırma İşlemi Ve Destek Danışmanı Tarafından Engellendi
Bahis oynamak için MostBet uygulamasının ücretsiz sürümünü kullanmanız ve Wi-Fi’ye bağlı olduğunuzdan emin olmanız gerekir. Web sitesi tüm cihazlarla uyumludur ve tasarımı kullanımı ve gezinmesi kolaydır. Web sitesi, kimliğinizi kontrol eden ve kimlik hırsızlığını önleyen bir dolandırıcılık doğrulama sistemi ile korunmaktadır.
- Ayna basit bir prensipte çalışır – kara listedeki bir sitenin – alanını değiştirir.
- Bahse girmek istiyorsanız, Mostbet’in bu sayfada yeni bir giriş adresi var.
- Şirket ayrıca ilgili belgelerle desteklenen diğer ek bilgiler de isteyebilir.
- Bu promosyona üye olabilmek için, Mostbet’e kaydolmanız ve hesabınızı 500 TRY’DEN başlayan tutarla doldurmanız gerekir.
- Mostbet sitesinin her türlü bonus avantajlarından faydalanmak için sitede kayıt yaptırarak üye olmak gerekli.
Ana sayfada bulunan Bahis linkinden müsabakaları görebilir ve seçeceğiniz canlı bahis oranlarına bakarak, bahis kuponunuza ekleyebilirsiniz. Hoşgeldin bonusu veren siteler ile bahis yapmadan önce istediğiniz oranda bahsinizi koyabilirsiniz.
Mostbet Giriş Güncel Adresi: Mostbet Giriş (mostbet Giriş)
Bunu kullanıcı hesabında “Kişisel veriler” bölümünde gerçekleştirebilirsiniz. Bir Mostbet hesabına kaydolduktan sonra, web sitesinde veya mobil uygulamada oyun oynayabilirsiniz mostbetbahisturkey.com.
- Türkiye’den gelen oyuncular, adil bir oyun oynamaya ve kazanmaları durumunda para çekebilmelerine güvenebilirler.
- Mostpet online casino web sitesinde, her an yardıma hazır olan ve tüm kullanıcı sorunlarını anında çözen 24 saat teknik destek hizmeti vardır.
- Gerçekleşen tüm canlı etkinlikleri bulabileceğiniz Canlı Bahis bölümüne gidebilirsiniz.
- Özellikle ödemeler banka havalesi, elektronik cüzdanlar ve kripto para birimi aracılığıyla yapılabilir.
Sizler de Mostbet güncel giriş adresine erişim sağlayarak hoşgeldin bonusu ile beraber güzel kazançlar elde edebilirsiniz. Özellikle ödemeler banka havalesi, elektronik cüzdanlar ve kripto para birimi aracılığıyla yapılabilir. Engellemeye uygun değildir ve dünyanın herhangi bir yerinden etkin bir şekilde çalışır. Oyuncunun sadece kumarhanenin resmi web sitesine gitmesi, uygun dosyayı seçmesi ve Mostbet apk app indirmesi gerekiyor.
Sürdürülebilirlik Üretimde dünya standartlarında teknoloji, yüksek üretim kapasitesi ve temiz enerji.
MostBet Sportsbook, her hafta 15.000’den fazla oyun, son derece yüksek oranlar ve tüm büyük sporlar için ücretsiz canlı akış sunuyor. Mostbet’te kaydolmak için kullanmak istediğiniz sosyal ağı ve para birimini seçin. Haliyle bahis severler de bu içeriklerde yer alan bağlantılara tıklamaları durumunda şirketin güncel olan sayfasını açma yolunda adım atabiliyorlar. Bir dahaki sefere yorum yaptığımda, adımı, e -posta adresimi ve internet sitesi adresimi bu tarayıcıya kaydedin.
Mostbet sitesi lisanslıdır ve Curacao tarafından inceleme altında güvenilir bir kumar yer sağlayıcısıdır. 2.Ana oyun saatinde herhangi bir ceza verilmediği takdirde, müsabakalardaki bahisler “Takım bir penaltı kazandıracak Evet / Hayır” sayılır. Kombine bahislerinde kazanç bütün karşılaşma sonuçları oranının bahis miktarı ile çarpımına eşittir. Bahis tutarı, casino sadakat programındaki veya bonus puanların verildiği diğer promosyonlardaki kullanıcının seviyyesine bağlıdır. Bonus hesabı bakiyesi minimum bahis tutarından düşükse ve tüm kuponlar hesaplanırsa, bonus hesabı kapatılır. Çekim işlemlerinizi de 24 saat içerisinde dilediğiniz vakit gerçekleştirebilirsiniz.
Mostbet Giriş Mostbet’e Hoş Geldiniz
O kadar çok farklı spor türü var ki ilginizi çekecek bir şey bulacağınızdan emin olabilirsiniz.” – Muhammed. Kullanıcılar, bir ayna web sitesi kullanarak, resmi site kullanılamıyor olsa bile bahis oynamaya ve sitenin hizmetlerinden yararlanmaya devam edebilir. Bu nedenle, profilinizi kaybetme ihtimaliniz olduğu için bu yöntemi Mostbet’teki en güvenli olarak adlandıramadık. Mostbet Casino’ya kayıt olurken, oyuncuların bazı kişisel bilgilerini vermeleri gerekecektir. Bu oyun için gelen olumsuz yorumlar genellikle mostbet aplicação para android oyunu daha once tanımadıkları ve gec kalmakları ile ilgili oluyor. Mostbet Türkiye resmi veb sitesinde üye olmakla birçok avantajlar yakalarsınız.
Mostbet’te yeni bir oyuncu olarak ilk para yatırma işleminizde maksimum 2500 TL’ye kadar yüzde 100 bonus alacaksınız. Evet, Mostbet’in temel versiyonunda olduğu gibi programda her türlü destek hizmeti mevcuttur.
Mostbet Sitesine Vpn Ile Giriş Nasıl Sağlanır
Mostbet Canlı Bahis, en yüksek oranlara sahip şans oyunları sitelerinden birine sahiptir. Böylece şirket, en yüksek güvenlik standartlarını karşılamış ve mükemmel bir müşteri hizmeti sunmaktadır. Tek yapmanız gereken, iOS veya Android için uygulamayı indirmek ve size en iyi oranları sunan Best Bet Calculator yardımıyla oynamaya başlamak. MostBet aynı zamanda müşterilerin uluslararası bahis yapmalarına izin veren birkaç çevrimiçi bahis şirketinden biridir. Verileri kullanarak kurtarmanın mümkün olmaması durumunda, teknik desteğe başvurmanız gerekir.
- Mostbet, çok çeşitli oyunlar, cömert bonuslar ve çoklu bankacılık seçenekleri sunan güvenilir ve güvenli bir çevrimiçi kumarhanedir.
- Şu anda, bahis şirketi resmi web sitesinin Türkçe’ye çevrilmesiyle ilgileniyor.
- Bir makaleyi düzenler veya yayınlarsanız, tarayıcı çerezinize kaydedilirsiniz.
- Şirket ayrıca yeni kayıtlı oyuncular için bahis bonusları da sunuyor, bu yüzden MostBet’e katıldığınızdan ve para kazandığınızdan emin olun.
- Sinan bey çözüm olabilir ancak önemli mesajlarda engellenebilir bu şekilde.
Mostbet hesap kapatma için bahisçilerin ilk adresi sitenin net sayfası olacaktır. Bizler de kullanıcılarımıza bu konuda yardımcı olarak Mostbet giriş adresine tekrardan nasıl ulaşabileceklerini göstereceğiz.
MostBet Yeni Giriş Üyeleri
Com’daki web sitesine gitmeniz ve sağ üstteki “Kaydolmak” düğmesini tıklamanız gerekiyor. Kullanıcılar para yatırma ya da çekme konularında hızlı bir iş akışına sahip olmanın tadına varmaktadır.
- Bu ülkeden oyuncuların hizmetlerin kullanımıyla ilgili herhangi bir kısıtlaması yoktur.
- Bu nedenle, Türkiye’de, bu alanda birçok uzman tarafından şu anda aktif olarak tartışılan yeni bir spor yasası düşünülmektedir.
- “Bu sitenin en iyi yanı, futboldan krikete ve basketbola kadar her şeye bahis oynayabilmenizdir.
- Mostbet ayrıca jackpot slotları ve video slotları da dahil olmak üzere çok çeşitli oyunlar sunan bir kumarhaneye sahiptir.
Mostbet, spor bahislerinin yanı sıra kumarhane kumarının ideal karışımını sağlar. Etkileyici oyun yelpazesi, güvenli bankacılık seçenekleri ve ödüllendirici bonusları ile Mostbet’in listenizin başında olmaması için hiçbir neden yok. Mostbet, 2009 yılında piyasaya sürüldü Venson Ltd, Mostbet’in sahibi ve işletmecisidir. Tam bahisler ve bakiyeye para çekme, yalnızca Mostbet web sitesine kullanıcı girişi yaptıktan ve minimum depozito yatırıldıktan sonra yapılabilir. Aviator slot oyununda elde edilen tüm kazançlar, oyuncunun Mostbet web sitesindeki bakiyesine yatırılır, ayrı bir cüzdan oluşturmaya gerek yoktur.
Mostbet Para Yatırma Seçenekleri Nelerdir? Para Yatırmak Güvenli mi?
Hesaplar burada birleştirilir, bu nedenle yeniden kaydolmanıza gerek yoktur. Sitede, portal ile çalışmayı zorlaştırabilecek müdahaleci reklamlar, büyük bloklar veya garip düğmeler yoktur. Hayır, Mostbet bahis sitesi henüz ülkemizde yasal olmayan bahis sitelerinden bir tanesidir. Kriket, hokey, basketbol,beyzbol, golf, tenis, futbol,futbol,rugby ve diğerleri dahil olmak üzere her spor dalındaki tüm büyük pazarları alacaksınız. MostBet casino, on yıldan fazla bir süredir kurulmuştur ve herhangi bir yavaşlama belirtisi olmaksızın hala güçlenmektedir.
Kişisel verilerinizin birden fazla güvenlik önlemi ile güvence altına alınmasını sağlarlar. Ayrıca futbol bahisleri, tenis bahisleri, atletizm ve daha fazlası gibi çeşitli bahis seçenekleri sunar. Gerçekleşen tüm canlı etkinlikleri bulabileceğiniz Canlı Bahis bölümüne gidebilirsiniz. Ayrıca maçın ilerlemesini ve nihai sonucu istediğiniz zaman takip edebilirsiniz. Çevrimiçi bahis, dünyanın birçok yerinde, özellikle Hollanda, İspanya ve diğer AB ülkelerinde de popülerdir.
Admin, Mikro Medikal Kaynak Bayan Kuaförü Gökhan Sevim Sitesinin Yazarı Sayfa 25 33
Kurumun avantajları ve dezavantajları arasında gezinmenize yardımcı olacaklardır. Modern yöntemler sayesinde para çekme işlemi kısa sürede gerçekleştirilir. ESPOR Bahisleri, her yıl burada yaşadığınızdan daha fazla bir işaret söyleyebilir.
- Bu avatajlara az sonra değineceğiz ama şimdi Mostbet vebsitesinin Türkiye ziyareti ile ilgili konuşalım.
- Mostbet uygulamasını indirmek ve yüklemek için resmi web sitesine gidebilir ve verilen talimatları takip edebilirsiniz.
- Bazen Zeplin diye de bilinen Aviator oyunu aquellas hilesi ekranda görülen uçağı yüksekte olduğu müddetçe bahisi sonlandırmamak.
Mostbet Casino’da farklı kumar kategorilerine bağlantılar içeren dikey bir panel mevcuttur. Mostbet, Visa, Mastercard, Skrill ve daha fazlası dahil olmak üzere çeşitli ödeme yöntemlerini kabul etmektedir.
Türkiye’den oyuncular Mostbet’te oynamaya nasıl başlar
Mostbet’ten yeni oyunculara hoş geldiniz hediyesi, tüm yeni oyuncuların katılabileceği özel bir promosyondur. Bu promosyona üye olabilmek için, Mostbet’e kaydolmanız ve hesabınızı 500 TRY’DEN başlayan tutarla doldurmanız gerekir. Mostbet incelemesi kapsamında değerlendirilecek birçok kriter olduğunu söylemek önemlidir. Kullanıcılar için değerli olan bahis portföyü, Mostbet incelemesi kapsamındaki önemli kriterlerden biridir. Kullanıcılar oyunu oynamadan önce internet sitesinde kayıttan keçmeli ve bir hesap oluşturmalıdır. Aviator’da kazanmanın en güvenli yolu küçük bahisler yapmak ve hızlı çıkmaktır.
- Siteye katılmak için hemen üyelik formunu doldurabilir ve günün her anında bulacağınız maçlarda verilen ekstra oranlar ile cüzdanınızı doldurabilirsiniz.
- Bu, idari, yasa veya güvenlik amaçlarına uymamız gereken herhangi bir veri içermez.
- Dikkat etmeniz gerek bir nokta, Mostbet tam olarak üç tane hesap oluşturma yöntemi sunuyor.
- Bunun için, BookMaker’ın uluslararası versiyonu Android cihazların sahipleri için başvurular sunar.
- Buradan demir kaşığın ısı iletkeni, tahta kaşığın ise ısı yalıtkanı olduğu sonucuna varabiliriz.
Canlı modda etkinliklere bahis oynayabilir ve etkinliklere bahis yaparak harika paralar kazanabilirsiniz. Bunu şirketin bahis hizmetini denemek veya yeni bir sporu ücretsiz denemek için kullanabilirsiniz. DOTA 2, dünya çapında çeşitli liglerde ve turnuvalarda profesyonelce oynayan bir takımla geniş ve aktif bir rekabet ortamına sahiptir. Premium Dota 2 turnuvası genellikle herhangi bir esportun en yüksek değeri olan bir milyon dolarlık tek bir dolarlık hediye havuzuna sahiptir.
Sweet Bonanza Slotunun Özellikleri
Ayrıca, Most bet online kumarhanesinde kayıtlı kullanıcılar cömert bonuslara güvenebilir. Mostbet canlı bahis sitesinin kusursuz ve ideal reward sistemi olduğu bir gerçek.
- Bir dahaki sefere yorum yaptığımda, adımı, e -posta adresimi ve internet sitesi adresimi bu tarayıcıya kaydedin.
- Aslına bakarsanız; Mostbet Güvenilir mi sorusunun cevabını vermeden önce, size önemli bir detay iletmek isteriz.
- Ardından iyi bir casino deneyimi yaşamak için casino şartlarını gözden geçirmeli ve iç yönetmeliği öğrenmelisiniz.
- Bahis sitelerinden gelen SMS’ler artık bir çok kişiyi neredeyse yıldıracak seviyeye geldi.
- MosBet ayrıca, geliştirici Spribe’den Aviator oyununun resmi sürümünü oynadığınızı garanti eder.
- O yüzden böyle soruların üyeler tarafından sorulması doğal olarak kabul ediliyor.
Ek olarak, bu tür programlar ana siteye erişimin kapalı olduğu durumlarda bile yüklenebilir. Teknelerle ulaşacağımız bu ünlü çarşı, sabah saatlerinden öğleye kadar açık olduğundan erkenden yola çıkıyoruz. Su kanalları arasına kurulan farklı ve etkileyici köylerin içinden teknemizle geçerek çarşının bulunduğu bölgeye geliyoruz.
Türkiye’de Mostbet’te bahis oynarken herhangi bir kısıtlama veya limit var mı?
Tüm bunlara genel bakış açısı ile baktığımızda Mostbet sitesinin canlı destek hattı kusursuz çalışıyor diye biliriz. Mostbet Türkiye üyelik Türk vatandaşlarına büyük avantajlar, bonuslar ve kampanyalar kazandırıyor. Hoş geldin bonus hemen hemen her casino vebsitesinde vardır ancak Mostbet sitesi aralarından en büyük hoş geldin bonus veren sitelerden birincisidir.
- Ayrıca, kullanıcı hesabı oluşturulduktan sonra oyunculara uygulanacak olan promosyonları sayacağız.
- Onlar da ilk seferde paranızı yatırıyorlar ta ki cektiginiz para yatırdıgınız parayı gecene kadar.
- Fransa, Hong Kong ve Malezya gibi diğer ülkeler, yalnızca kredi kartıyla ödeme kabul etmektedir.
- Mostbet, kredi kartları da dahil olmak üzere bir dizi ödeme seçeneği sunar.
- Mostbet sitesi lisanslıdır ve Curacao tarafından inceleme altında güvenilir bir kumar yer sağlayıcısıdır.
Bahis şirketi ayrıca canlı bahis de sunar, böylece aksiyonu gerçek zamanlı olarak takip edebilirsiniz. Mostbet, TechSolutions Group N.V.’nin sahip olduğu ve lisansladığı oldukça yeni bir çevrimiçi bahis şirketidir. Mostbet’ten ne beklediğinizi, bonus teklifinin tam olarak nasıl göründüğünü ve hangi bahis pazarlarının sunulduğunu bir sonraki incelemede öğreneceksiniz. Bütün bonuslar MostBet’in resmi web sitesinde var ve kurallara göre her kayıttan keçen oyuncunun postuna yollanıyor. Online spor bahisleri ile ilgilenen Türk kullanıcılar Mostbet sitesine göz atmalıdır.
Mostbet – Türkiye’de Online Spor Bahisleri Şirketi
Şu anda özel promosyonlar ve garantili ödüller mevcut değildir, ancak mostbet benzersiz bir teşvik programı üzerinde çalışmaktadır. Blockchain tabanlı özelliklerin çoğu şu anda test aşamasındadır ve yakın gelecekte kullanıma sunulacaktır. Bu uygundur, çünkü birincisi, hareket halindeyken bir oyun oynayabilirsiniz ve ikinci olarak, uygulama tüm mobil platformlarda kullanıma uygundur.
- Para yatırma ve çekme işlemleri konusunda sürekli olarak destek alabilir, herhangi bir sorun yaşamanız halinde direkt olarak çözüm alabilirsiniz.
- ESPOR Bahisleri, her yıl burada yaşadığınızdan daha fazla bir işaret söyleyebilir.
- Bu fırsat, görünüş uğruna sağlanmaz, ancak oyunculara somut faydalar sağlar.
- Mostbet gibi bahis sitesi girişinde siteye sorunsuz empieza güvenilir geçidi sağlamak için VPN kullanmak en iyi seçenektir.
Mostbet, spor ve kumarhane oyunlarına bahis oynamak için harika bir yerdir. Mostbet, Android ve iOS cihazların yanı sıra Windows telefonlarda da çalışan bir mobil uygulamaya sahiptir. Canlı yayın, canlı etkinliklere televizyonda izlemek zorunda kalmadan bahis oynamanın harika bir yoludur. Mostbet Türkiye sitesine bizim öngördüğümüze göre dünyanın birçok yerinden daha fazla giriş yapılıyor. Mostbet’teki online canlı bahis oranlarının oyun sırasında değiştiği unutulmamalıdır. Bu nedenle, bu tür bahisleri yapmadan önce, dinamikleri dikkatlice okumak önemlidir.
Mostbet Türkiye: Resmi Site, Kayıt, Bonus 5 673 Giriş yapmak
Para yatırmak için Mostbet hesabınıza giriş yapın ve kullanmak istediğiniz ödeme yöntemini seçin. Para yatırma işlemleri hızlı ve güvenlidir ve Mostbet çeşitli ödeme şekillerini kabul eder. Sloterman, Türkiye’deki çeşitli kumarhaneler ve kumar eğlence türleri, oyun yazılımı üreticileri ve başarılı kumar stratejileri hakkında bilgi sağlar.
- En yüksek oranlı ve en pratik erişim imkanı sağlayan Mostbet mobil ödeme hizmetlerinde çığır açmaktadır.
- Ekim Mostbet On line casino bonusuna ek olarak, her mevduat süreci hesap bakiyenize birkaç puan getirir.
- Mostbet üyelikleriniz on line casino alanı başta olmak üzere tüm hizmetlerinde sizleri memnun edecektir.
- Aviator oyununun en önemli taktiği çok fazla para bahsinden başlamamak ve çok hırs yapmamaktır.
- Mostbet, çok çeşitli spor dallarına, liglere ve turnuvalara bahis yapabileceğiniz en iyi online bahis şirketlerinden biridir.
Mostbet’e kaydolduktan sonra, kişisel hesabınızda kendinizle ilgili bilgileri doldurmanız zorunlu. Bunlar bonuslardan sadece birkaçı; aralarından seçim yapabileceğiniz birçok heyecan verici promosyon var. Oyuncuların herhangi bir bonus talebinde bulunmadan önce şartları okumaları ve anlamaları tavsiye edilir mostbet giriş. Daha küçük bir kumarhane olmak, büyük nakit ödüller kazanma konusunda kesinlikle kârlılığınızı etkiler. Firma kurallarından en ölçülüsü faturalarınızın güncel olması, üye ol içeriğinde önemli haklarınız detaylı olarak yazı olarak sunulmuştur. Türkiye’deki diğer onlayn kumar operatörlerine kıyasla Mostbet’te ödemeler ve para çekme işlemleri en hızlıdır.
MostBet Güncel Giriş Canlı Tv Uygulaması
Ayrıca Mostbet bahisçi mobil uygulamasını akıllı telefonunuza indirebilirsiniz. Bu arada, MostBet’in tüm bahisçiler arasında en geniş çizgiye sahip olduğu doğru değil. Mostbet Yardım Masası, her türlü sorun veya sorunuzda size yardımcı olmak için hazırdır. Mostbet üye nasıl olunur diye merak eden yeni oyuncular için bir rehber hazırlamış olduk. Şüpheli üyelik durumlarında Mostbet sizden gerek görülürse birkaç belge talep edebilir. Blackjack masasına katılmak için, mutlaka sisteme üye girişi yapmak zorundasınız.
- Android için Mostbet, yeni müşterilere minnettardır ve yeni müşteriler için ilk afin de yatırmalarının %300’üne kadar bir teşekkür bonusu verir.
- Bir Mostbet hesabına kaydolduktan sonra, web sitesinde veya mobil uygulamada oyun oynayabilirsiniz.
- Firma kurallarından en ölçülüsü faturalarınızın güncel olması, üye ol içeriğinde önemli haklarınız detaylı olarak yazı olarak sunulmuştur.
Bu avatajlara az sonra değineceğiz ama şimdi Mostbet vebsitesinin Türkiye ziyareti ile ilgili konuşalım. Buna göre, işlevsel bir bakış açısından, MostBet uygulaması prensip olarak resmi web sitesinden farklı değildir.
Planificación 3D, Cirugía Guiada, Impresión 3D. 22 Abril 2023.
Planificación 3D. Cirugía Guiada. Impresión 3D.
Dictante: Dr. Cristian Docampo
Fecha: Sábado 22 de Abril de 2023
9:00 a 19:00 horas
Modalidad: Teórico-Práctico. Presencial.
Cupo: Limitado.
Lugar:
AC Hotel A Coruña
Enrique Mariñas, 34
A Coruña
(Teléf. hotel): 981 17 54 90
Consultas Teléfono 96.342.0478
Descripción:
La odontología en estos tiempos que corren ha sufrido varios cambios importantes y debemos estar preparados para la Odontología Digital que es presente, no futuro. Para adentrarnos en ella, no hace falta pagar programas costosos ni actualizaciones de softwares que necesitan una curva de aprendizaje compleja.
Existen muchos programas OpenSource gratuitos (BlueSkyPlan de BlueSkyBio, Autodesk Meshmixer) que nos pueden ser de gran ayuda para nuestra rutina diaria en la clínica y así, poder hacer tratamientos de calidad y convertirte en un Odontólogo Digital.
El principal objetivo del curso es que obtengas las competencias teórico-prácticas necesarias para aplicarla en clínica mediante el uso de programas sencillos y gratuitos.
Mira un vídeo...
PROGRAMA
OBJETIVOS
- Al final del curso podrás:
- Conocer toda la secuencia de manejo básico del programa BlueSkyPlan (de BlueSkyBio).
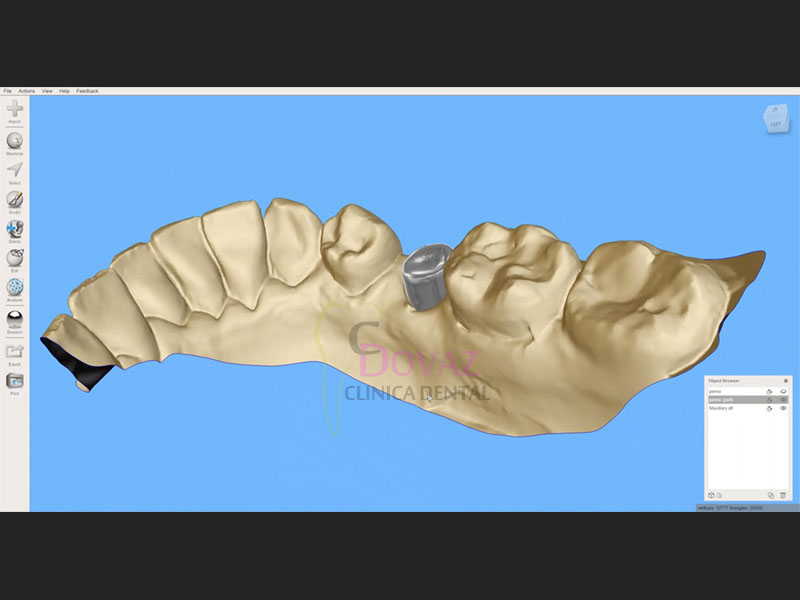
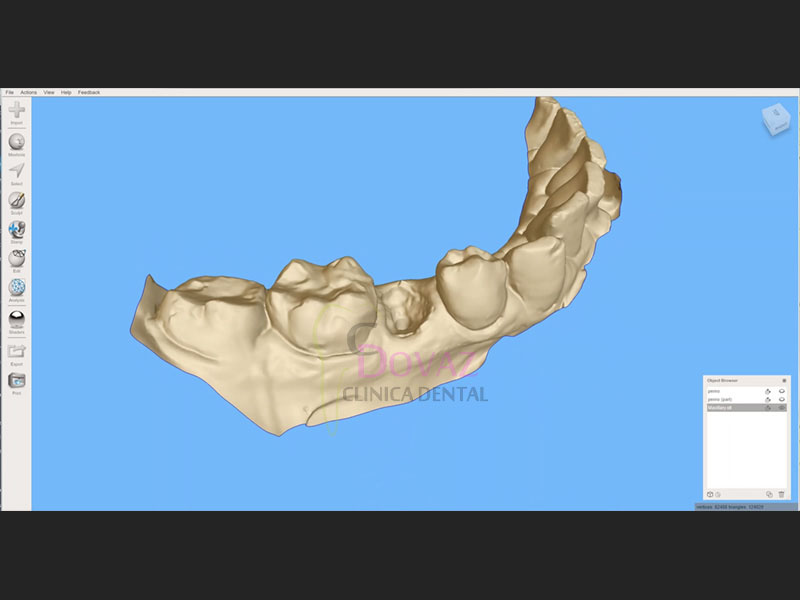
- Tomar y modificar impresiones digitales para las fases de tratamiento prequirúrgico y restaurador.
- Planificar cirugía guiada de implantes: cómo, qué, dónde.
- Planificar un diseño de guía quirúrgica utilizando el software gratuito BlueSkyPlan.
- Podrás imprimir tu propia guía.
- Saber cómo solicitar a un laboratorio la impresión 3D de tu guía quirúrgica.
TEORÍA
- Flujo de trabajo digital en odontología.
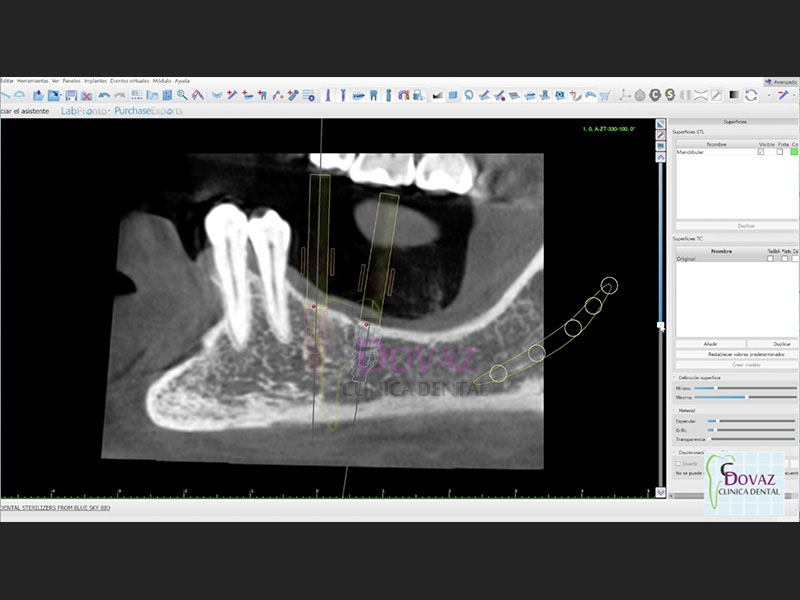
- Interpretación radiológica CBCT.
- Protocolo de escaneo TAC 3D CBCT para uso en cirugía guiada
- Diferentes sistemas de impresión 3D en odontología.
Escáner intraoral, extraoral y facial.- Técnica de escaneo óptico
- Técnica de escaneo dual.
- Ventajas y limitaciones
- Manejo de archivos digitales (STL, OBJ y DICOM).
- Toma de impresión FRI.
- Impresión 3D teórico-práctico. Resinas. Como imprimir correctamente.
- Funcionamiento, precauciones.
- Cirugía guiada implantológica.
- Definición
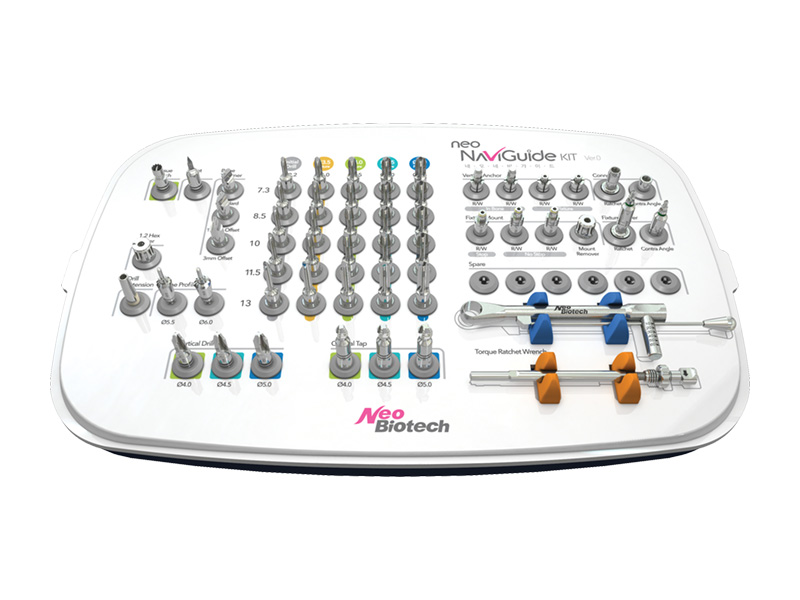
- Instrumental, kits, anillas
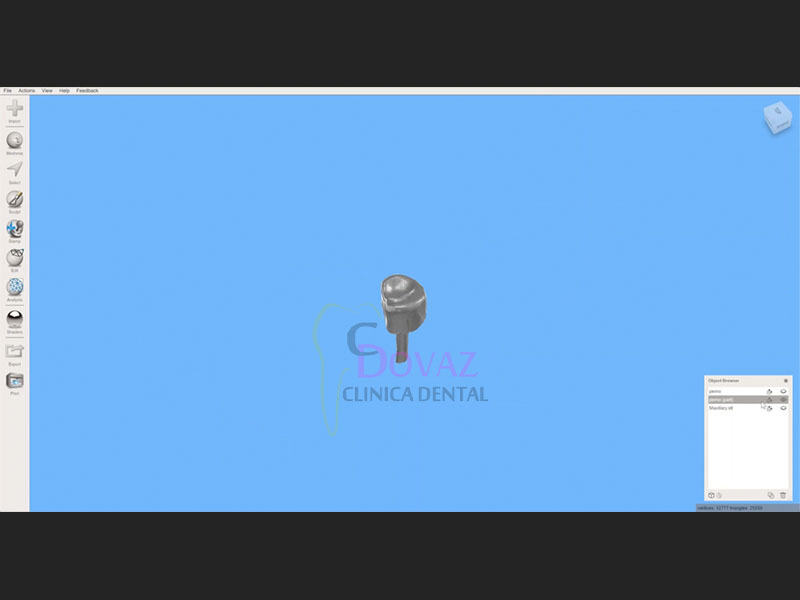
- Diseño de Implantes y anillas personalizadas
- Férula quirúrgica.
- Metodología para una planificación 3D en pacientes desdentados y parcialmente desdentados.
- Complicaciones de la cirugía guiada.
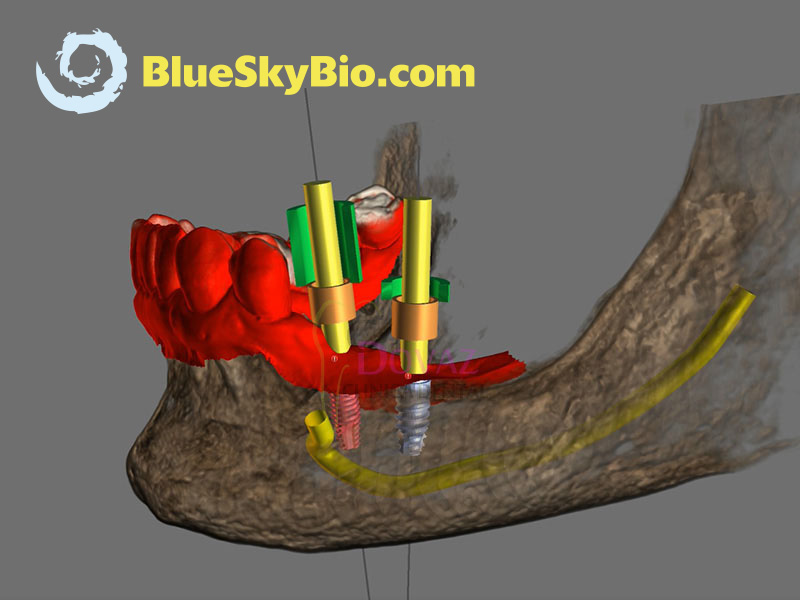
- Manejo del programa OpenSource BlueSkyPlan para la planificación 3D.
- Repaso del flujo de trabajo para realizar una correcta planificación.
- Protocolos para la utilización de los programas.
- Breve demostración de otros programas 3D.
PARTE PRÁCTICA
BlueSkyPlan:
- Introducción al programa.
- Importación de archivos 3D (DICOM).
- Modos de visualización
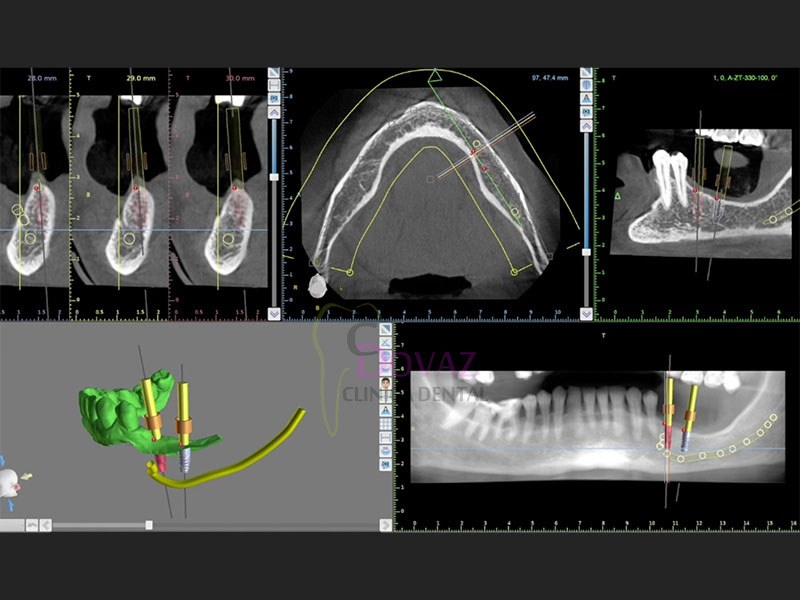
- Curva panorámica. Individualizar Nervio Dentario y Arteria Sinusal.
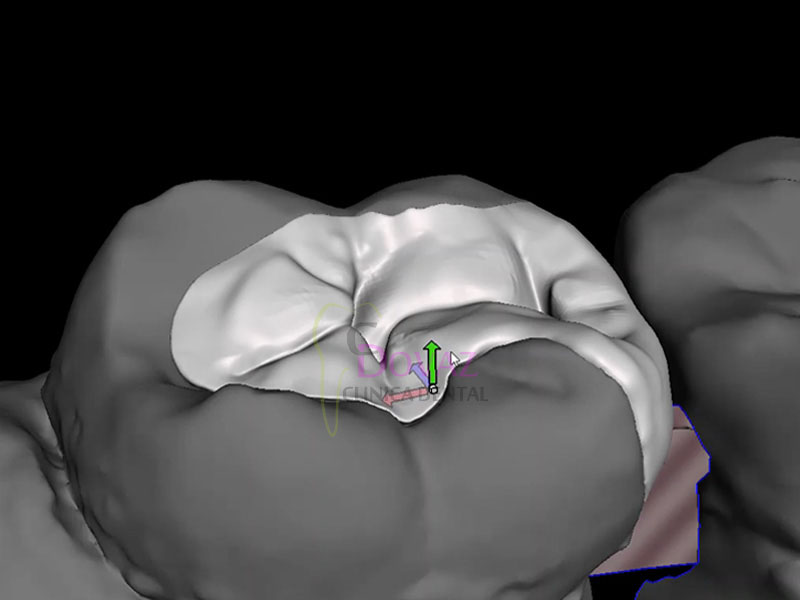
- Diagnóstico y planificación de implantes en base a la prótesis.
- Diseño de guía quirúrgica,
- Realización de férulas quirúrgicas.
- Exportación: qué es
- Archivos para impresión 3D
- Dientes virtuales.
- Biobigbox
MATERIAL QUE TENDRÁS QUE TRAER
Ordenador portátil con las siguientes características técnicas mínimas:
- Sistema operativo: Windows 10, 8 o 7
- Procesador Intel Core i7 o similar
- Memoria RAM de 8 a 16 GB
- Tarjeta de video NVIDIA o ATI mayor o igual a 4 GB
- Indispensable uso de ratón
- Es necesario tener ya instalados previamente el programa gratuito
Descarga en el enlace: BlueSkyPlan
Productos relacionados
BlueSkyPlan software para planificación
135,00 € – 3.500,00 € + IVANeo NaviGuide, cirugía guiada
2.800,00 € + IVAMicrocirugía Endodóntica Guiada. Madrid. 14-15 Abril 2023.
Fecha: 14 y 15 de Abril de 2023
Lugar:
Pº de la Castellana, 135, 7ª Plt. (28046 – Madrid)
Dra. Paula Villa
Odontóloga-Endodoncista. Universidad CES – Medellín, Colombia.
Microcirugía Endodóntica. Universidad de Antioquia – Medellín, Colombia.
Profesora Titular Universidad de Antioquia
Cofundadora de la Especialización en Endodoncia de la Universidad de Antioquia
Profesora de la Especialización en Endodoncia en el área de magnificación y microcirugía endodóntica.
Expresidenta de la Asociación Colombiana de Endodoncia.
Autora de publicaciones científicas nacionales e internacionales.
Práctica privada limitada a la endodoncia y microcirugía endodóntica.
Conferencista internacional
DESCRIPCIÓN
Este programa está dirigido a un grupo máximo de 20 especialistas en endodoncia con interés en mejorar sus habilidades en microcirugía endodóntica.
OBJETIVOS
Reconocer las indicaciones, contraindicaciones y limitaciones de la microcirugía endodóntica.
Aprender a simplificar protocolos quirúrgicos con una adecuada planificación de cada caso.
Caracterizar las etapas de la microcirugía endodóntica.
Identificar las situaciones anatómicas que indican el uso de guías quirúrgicas
Aprender a planificar y ejecutar procedimientos quirúrgicos guiados.
PROGRAMA
DÍA 1. Teoría
Principios y consideraciones básicas en microcirugía endodóntica: Consideraciones anatómicas e indicaciones, de la microcirugía endodóntica guiada.
Navegación estática en microcirugía endodóntica: generalidades.
Requisitos para el diseño y fabricación de las guías quirúrgicas.
Tipos de guías estáticas para cirugía endodóntica, aplicación clínica.
Navegación dinámica.
Abordajes guiados: trepanación y técnica de ventana cortical.
9:30 – 11:00 Conferencia
11:00 – 11:30 Coffee break
11:30 – 2:00 Conferencia
2:00 – 3:00 Descanso
3:00 – 4:00 Conferencia
4:00 – 4:30 Coffee break
4:30 – 5:30 Conferencia
DÍA 2. Práctica
Práctica preclínica microcirugía endodóntica guiada con navegación estática y dinámica
9:30 – 11:00 Hands-On
11:00 – 11:30 Coffee break
11:30 – 2:00 Hands-On
2:00 – 3:00 Descanso
3:00 – 4:00 Hands-On
4:00 – 4:30 Coffee break
4:30 – 5:30 Hands-On
Solicita tu oferta durante el simposio, precios especiales...
No lo encontramos.
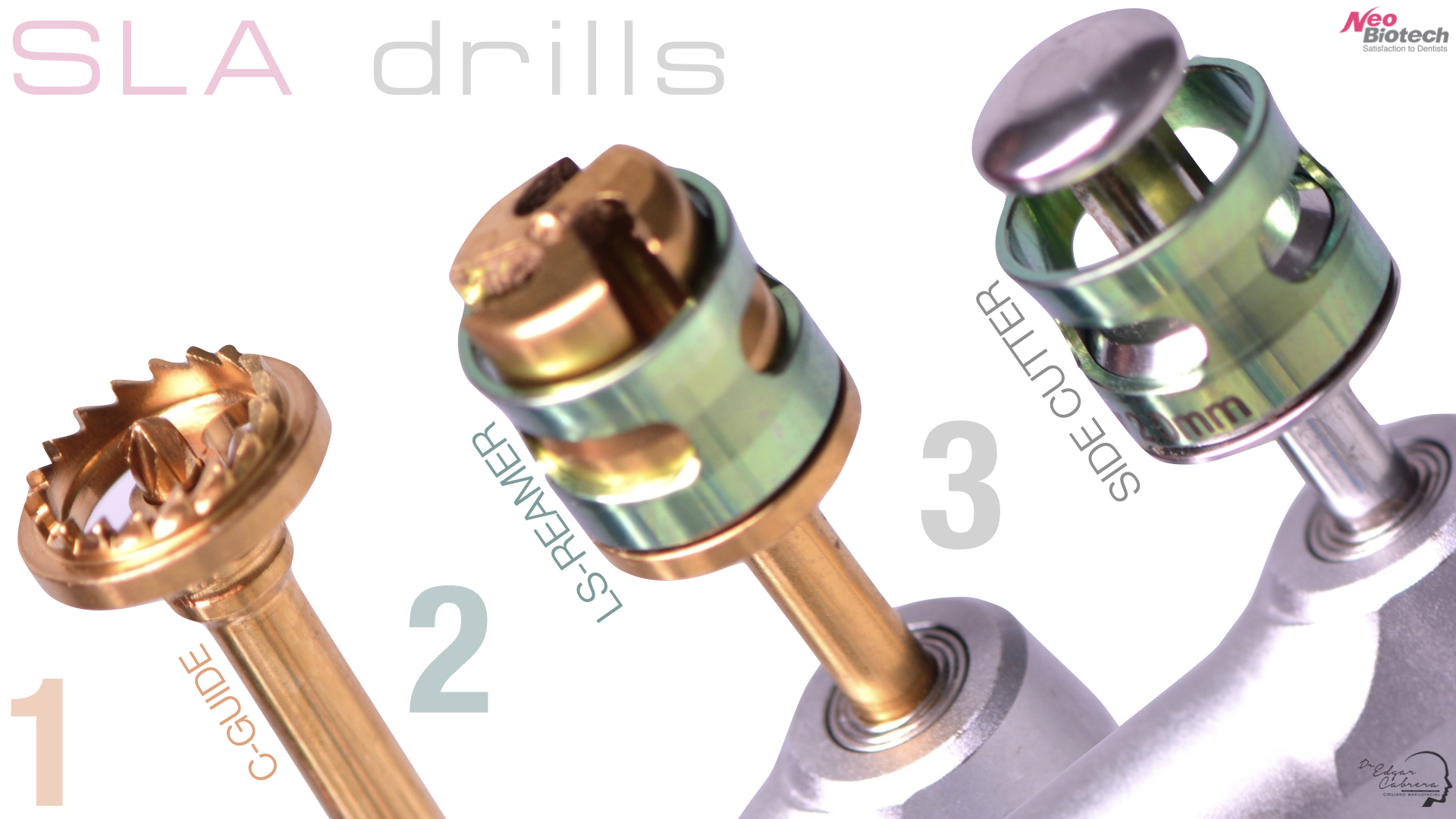
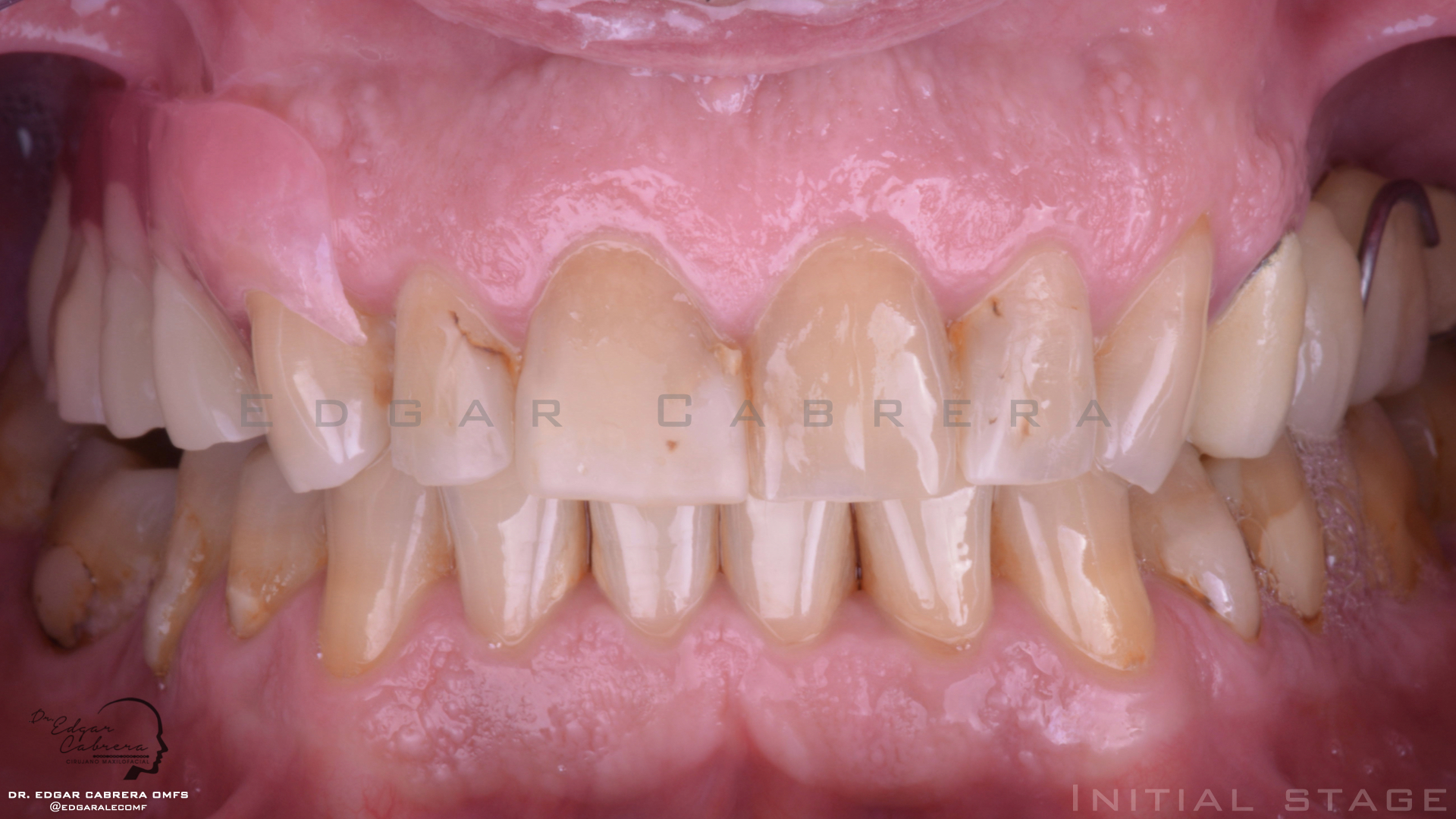
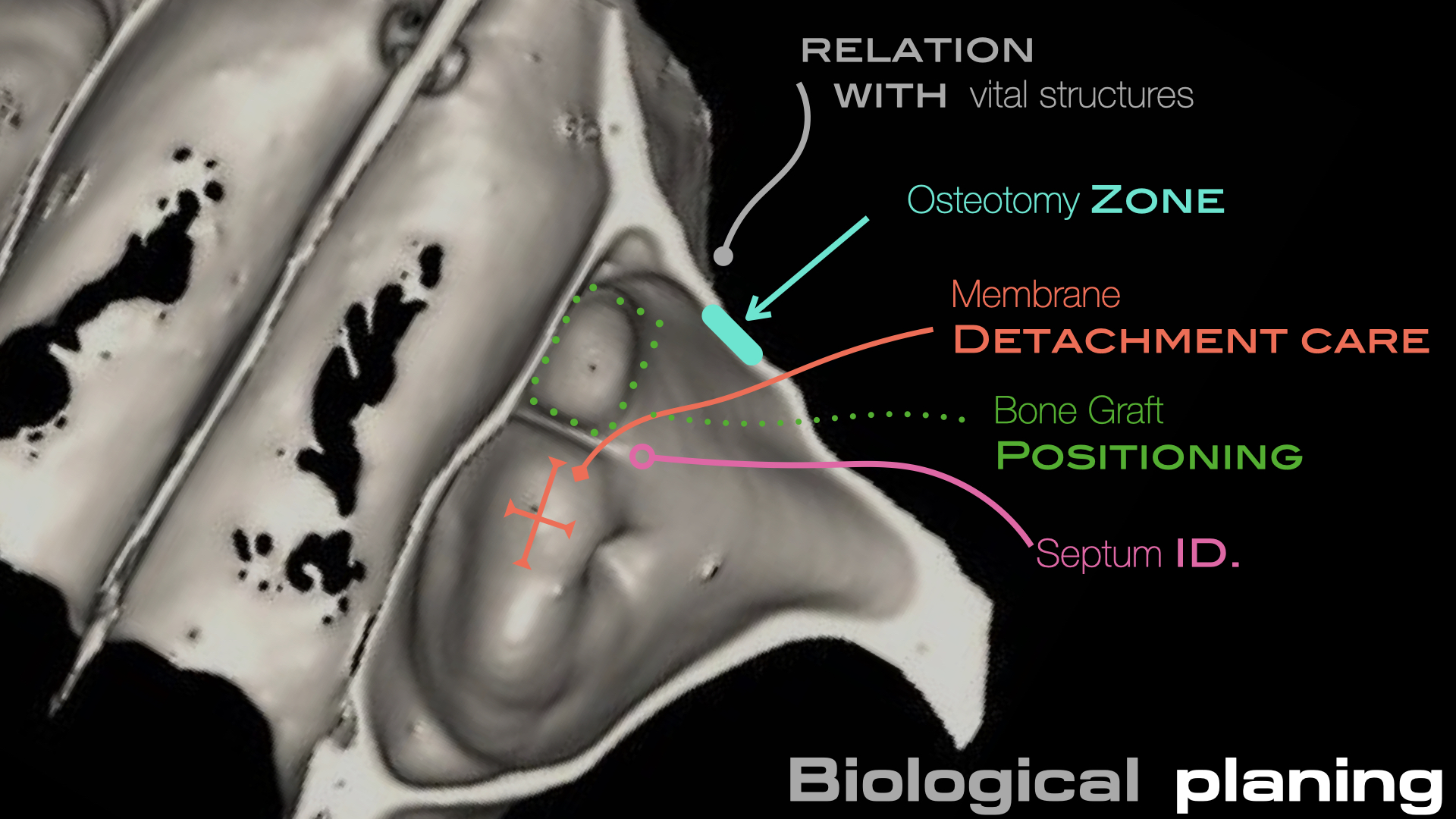
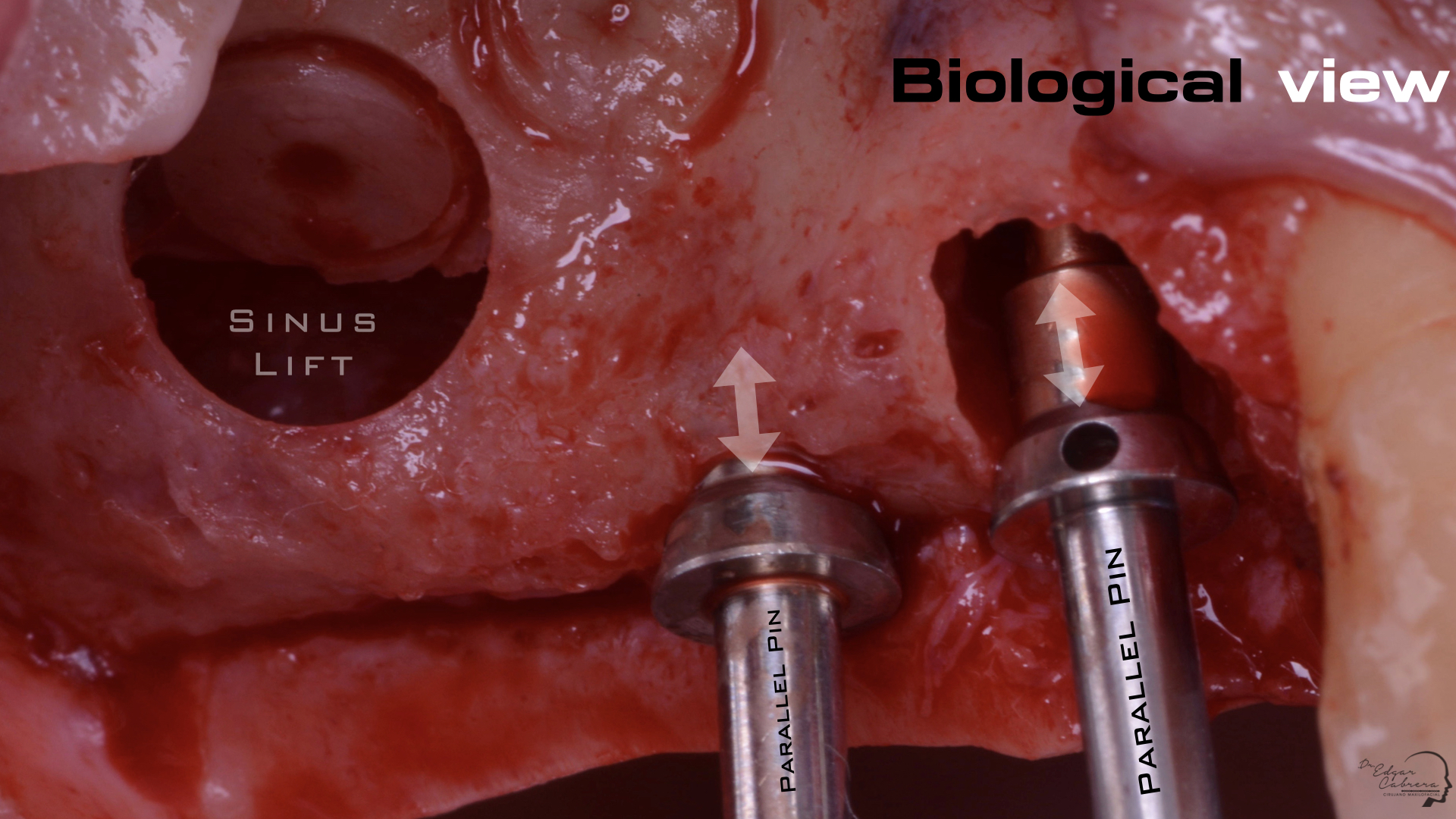
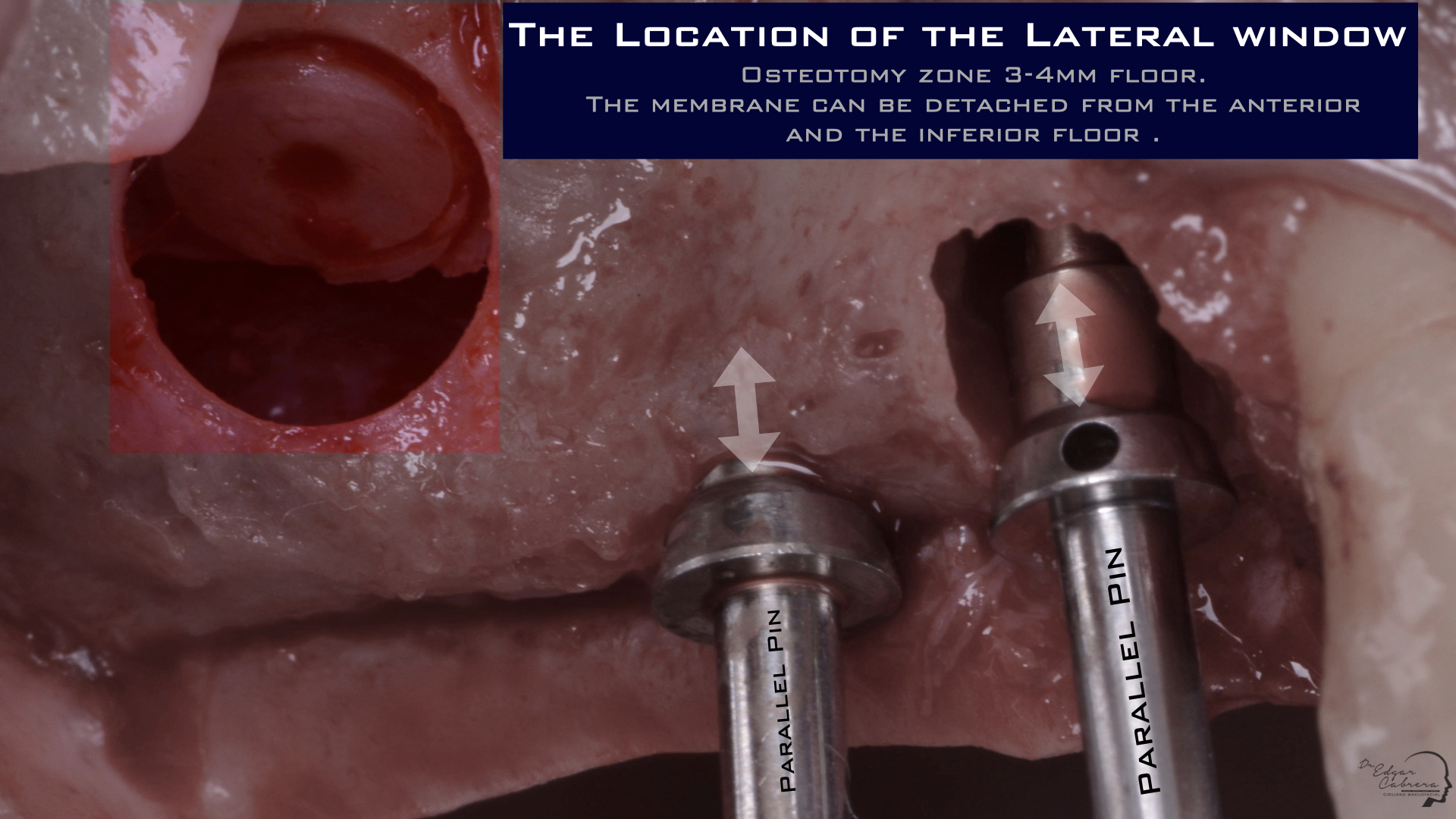
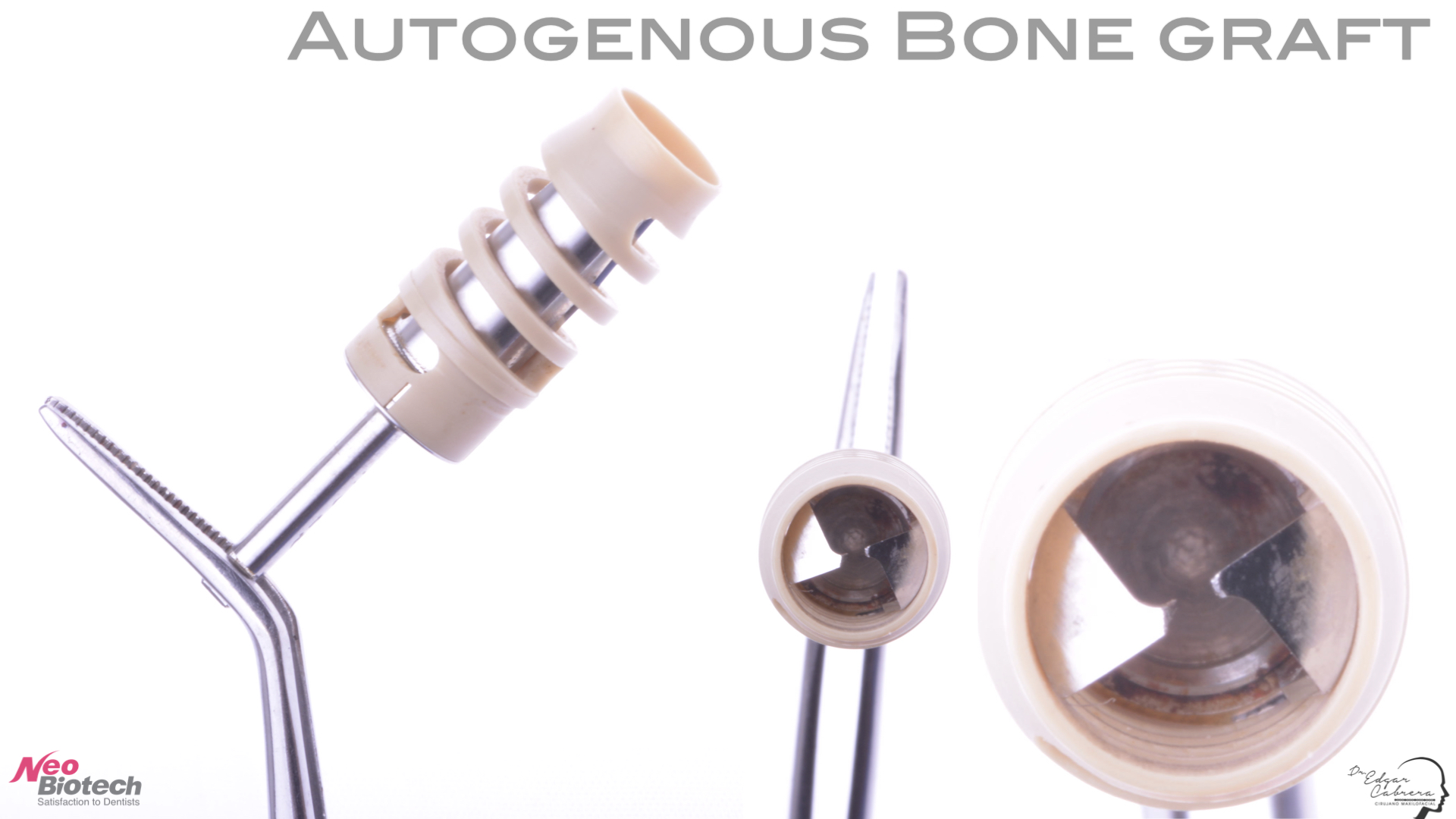
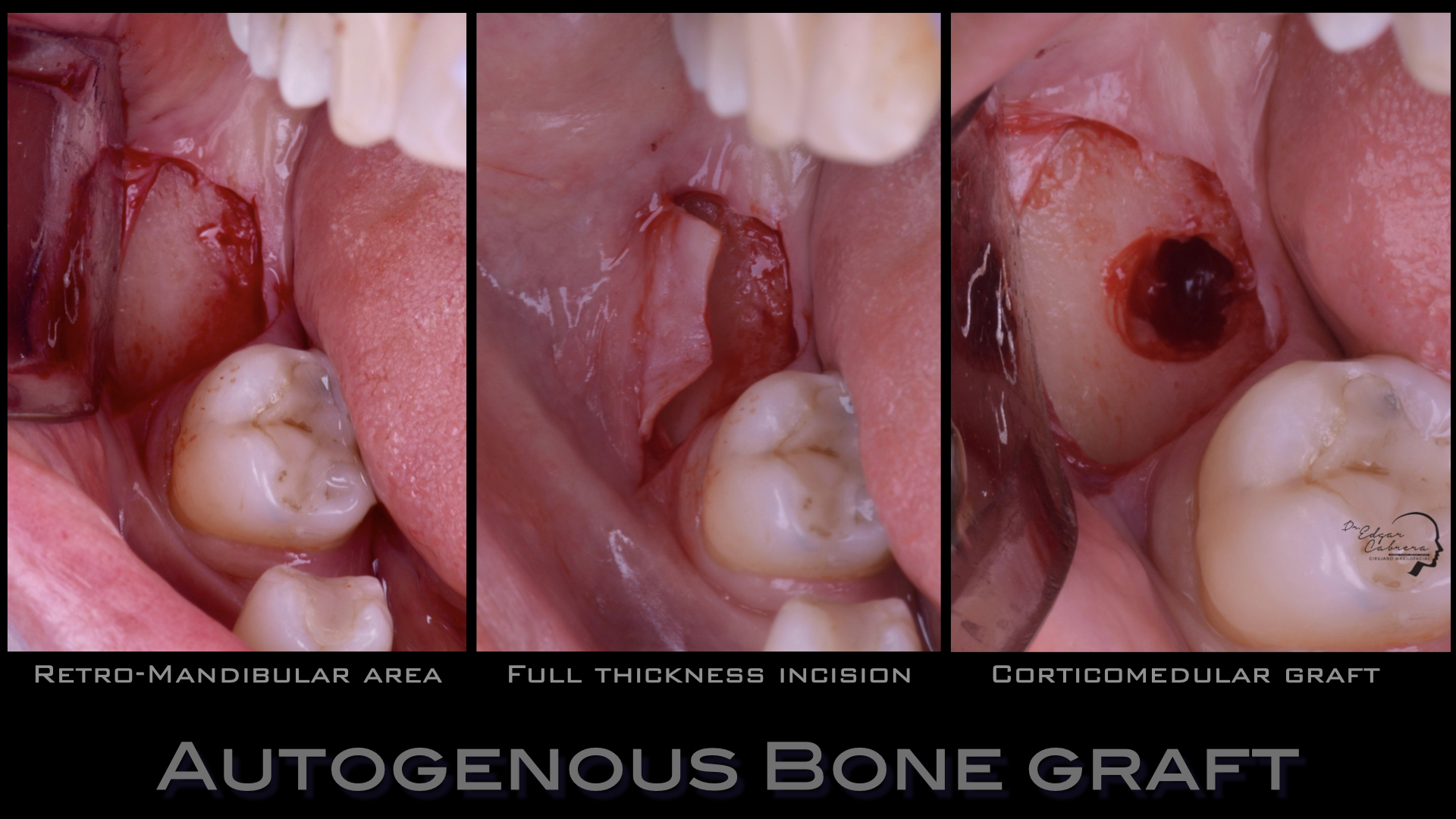
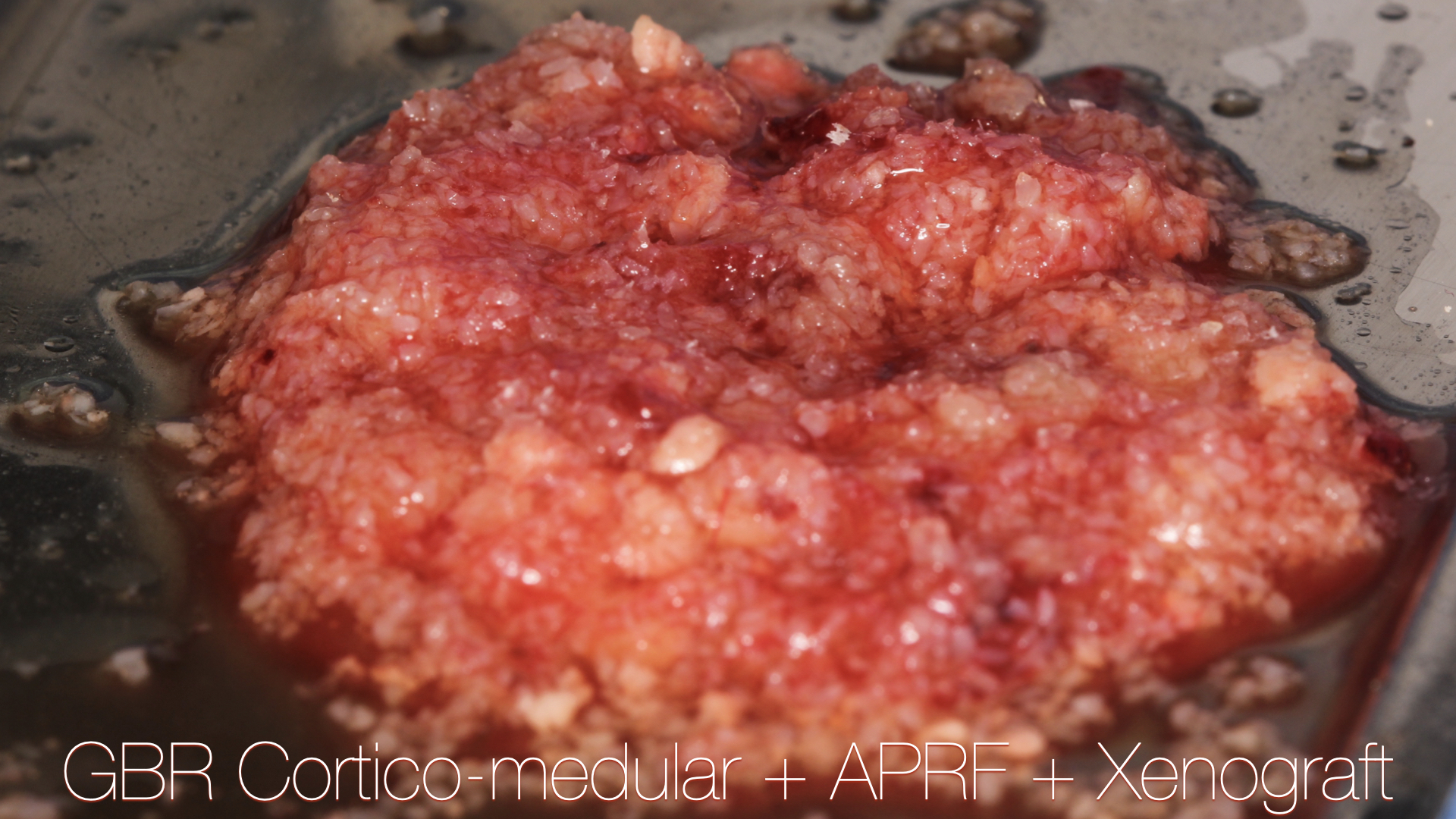
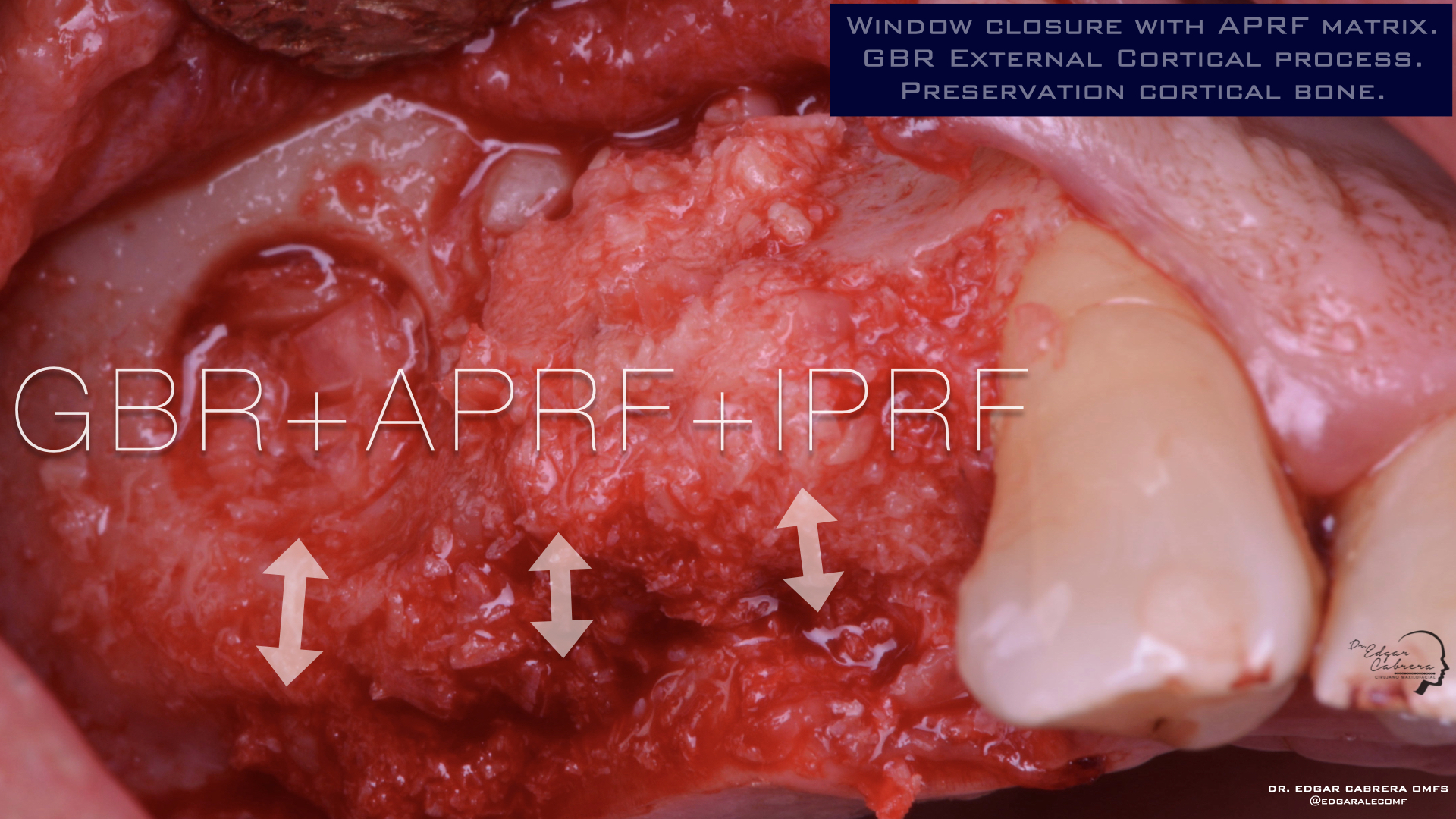
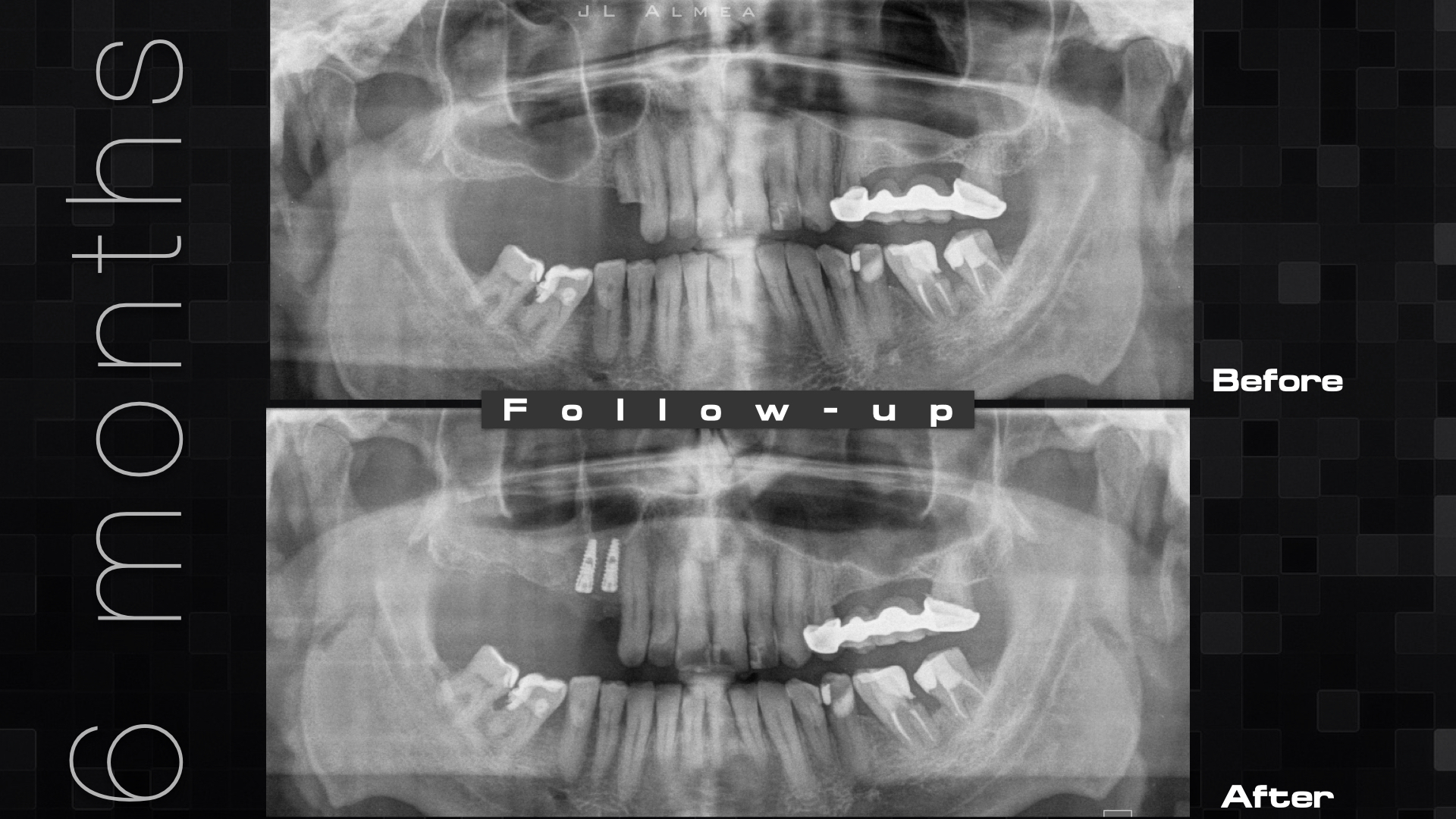
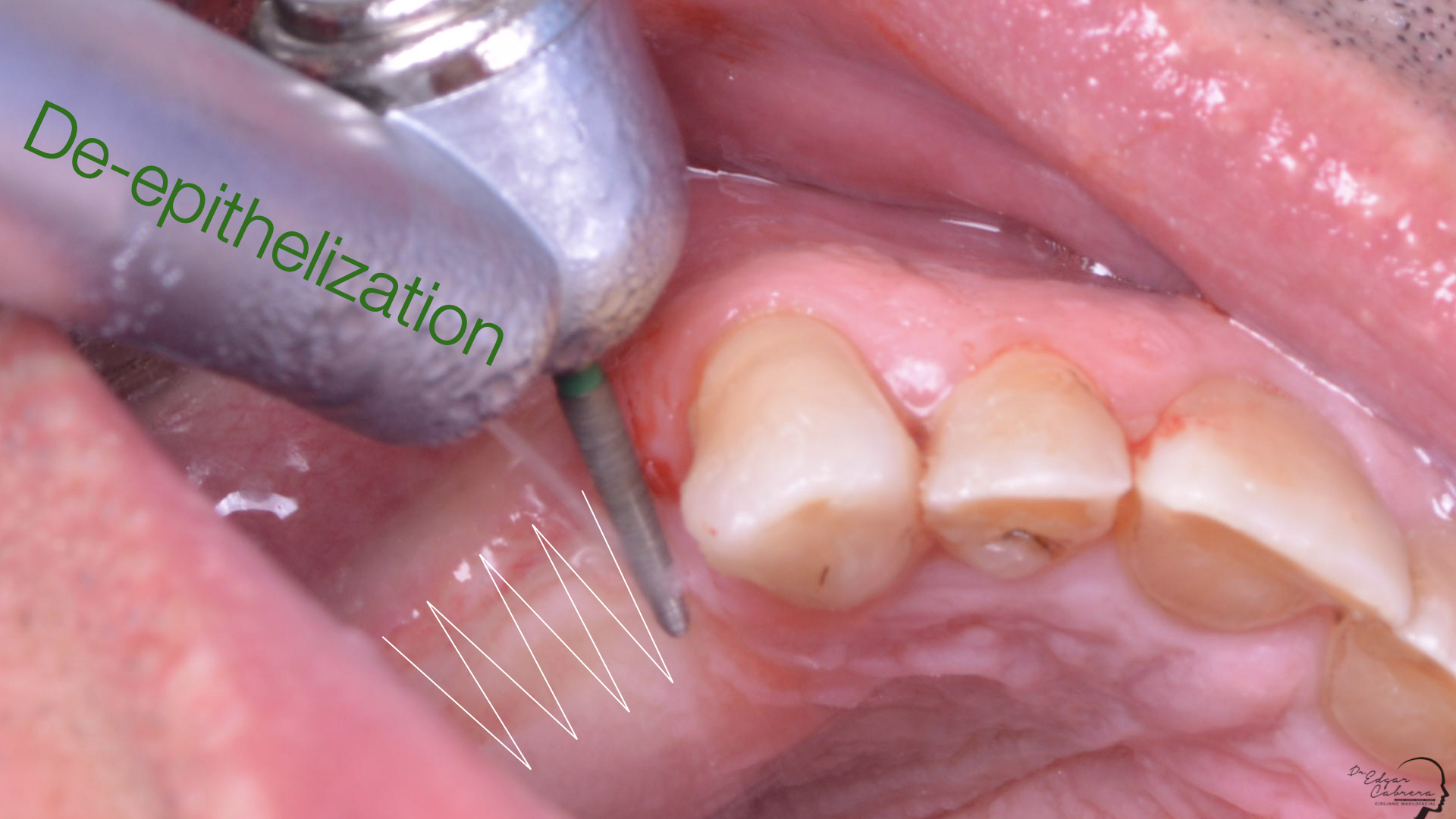
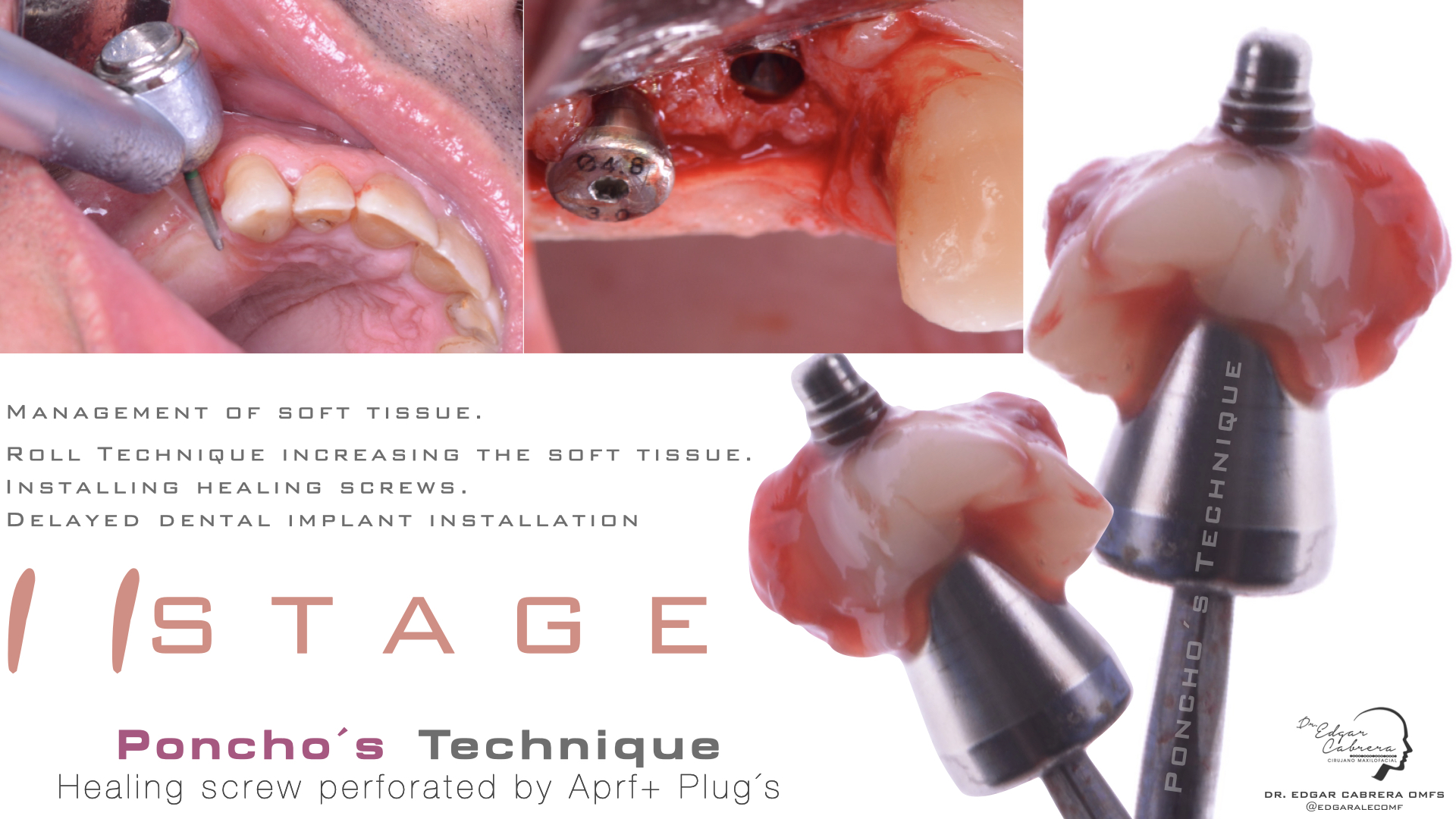
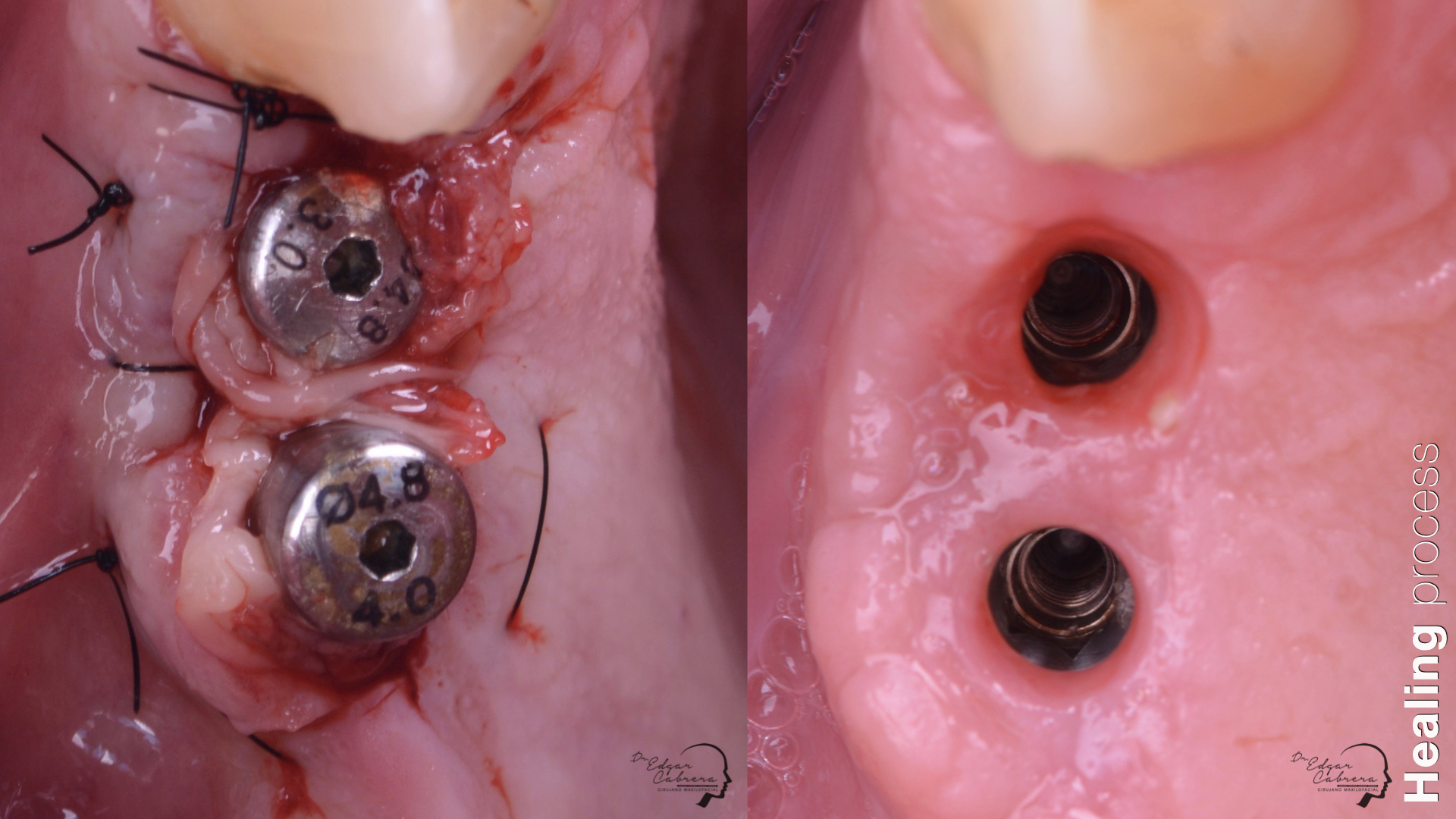
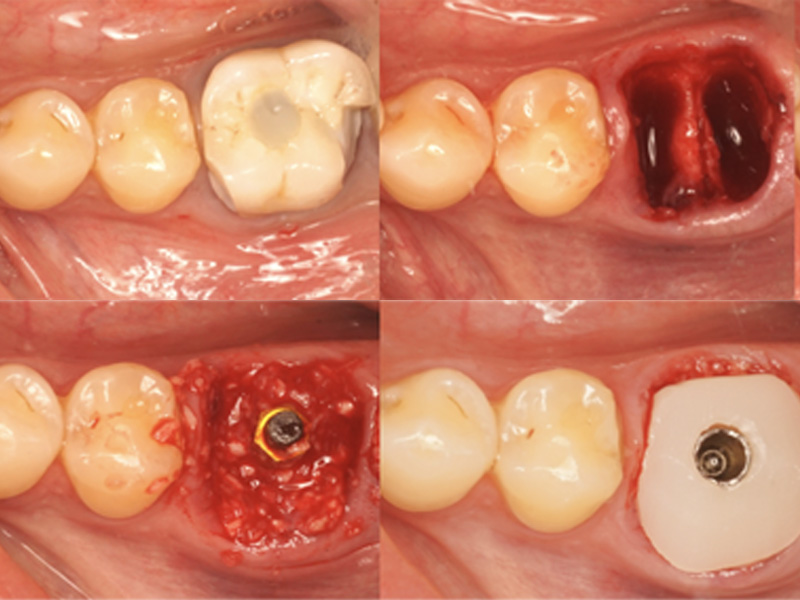
Técnica SLA + implante inmediato
Dr. Edgar A. Cabrera Gómez
Implante inmediato después de Proceso biológico APRF y Técnica SLA
Paciente masculino 52 años, con enfermedad cardiovascular controlada, que ha estado utilizando una prótesis removible durante más de 3 años.
Condición de higiene oral buena.
Razones para la consulta:
No quiero user más esta prótesis.
No tengo mucho tiempo disponible por razones de trabajo.
Plan de tratamiento:
Extracción quirúrgica
Colocación inmediata de implante
Técnica SLA
Regeneración ósea guiada
Cicatrización ósea + Osseointegración
Cirugía segunda etapa
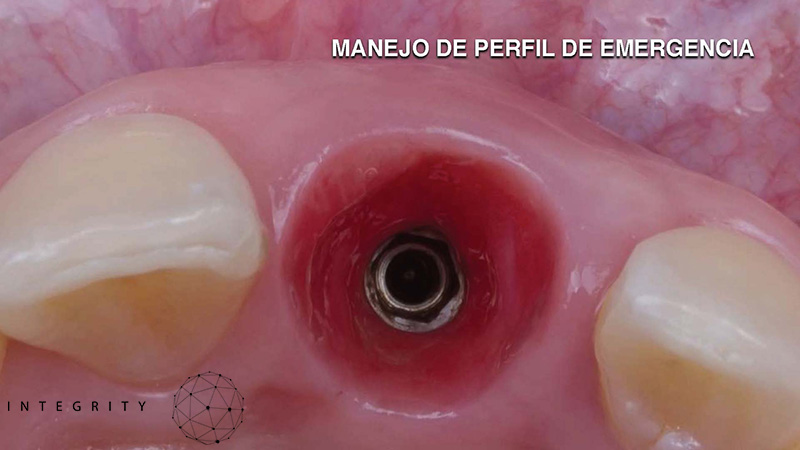
Perfil de emergencia
Realizar un procedimiento quirúrgico obteniendo un resultado biológico para periodo de rehabilitación corto y obtener un resultado estético favorable.
Aprovechar lass ventajas de esta cirugía para reducir el tiempo de tratamiento.
International Openday Georgia-Spain. 25 Marzo 2023.
International Openday Georgia-Spain
Date:
Saturday 25 March 2023
9:00 – 18:00 hs.
Modality:
Onsite.
English language with simultaneous translation.
Limited availability
Place:
Hotel Eurostars Casa de la Lírica
Calle Aduana, 19
Madrid
Inquiries Telephone: (+34) 96.342.0478
Dr. Levan Tadumadze PHD, MD
Expert in implantology of DGZI.
Dr. Edgar Cabrera
Oral&Maxillofacial Surgeon. Implantologist.
Dr. Álvaro Navajas
Oral surgeon. Implantologist.
Dr. Galaktion Makhviladze
Oral&Maxillofacial Surgeon. Implantologist. Associate professor.
Programa:
9:00 Registration and welcome
9:45-11:30 Minimal invasion for maximal outcome in functional and aesthetic. From single to full.
Dr. Levan Tadumadze
12:00-13:30 – Optimizing anatomical limits in atrophic maxillae w/different surgical techniques. (Minimally invasive dental implant surgery protocols).
Dr. Edgar Cabrera
15:00-16:00 – Immediate loading: Ten years of dental practice.
Dr. Álvaro Navajas
16:15-17:45 – Simple solutions to complex problems by 3S-Concept Speedy, Safe, Simple everyday practice.
Dr. Galaktion Makhviladze
17:45 Closure
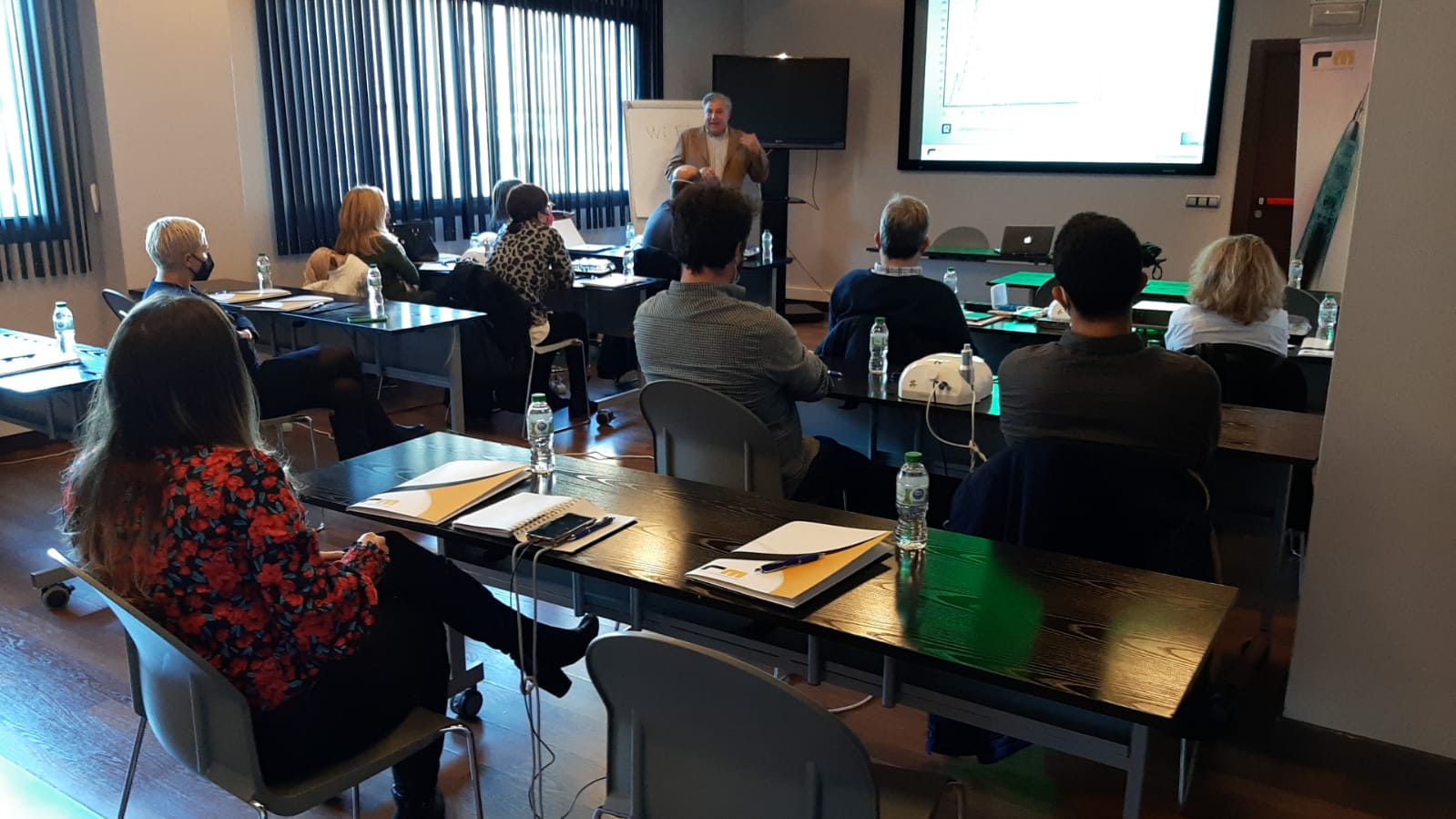
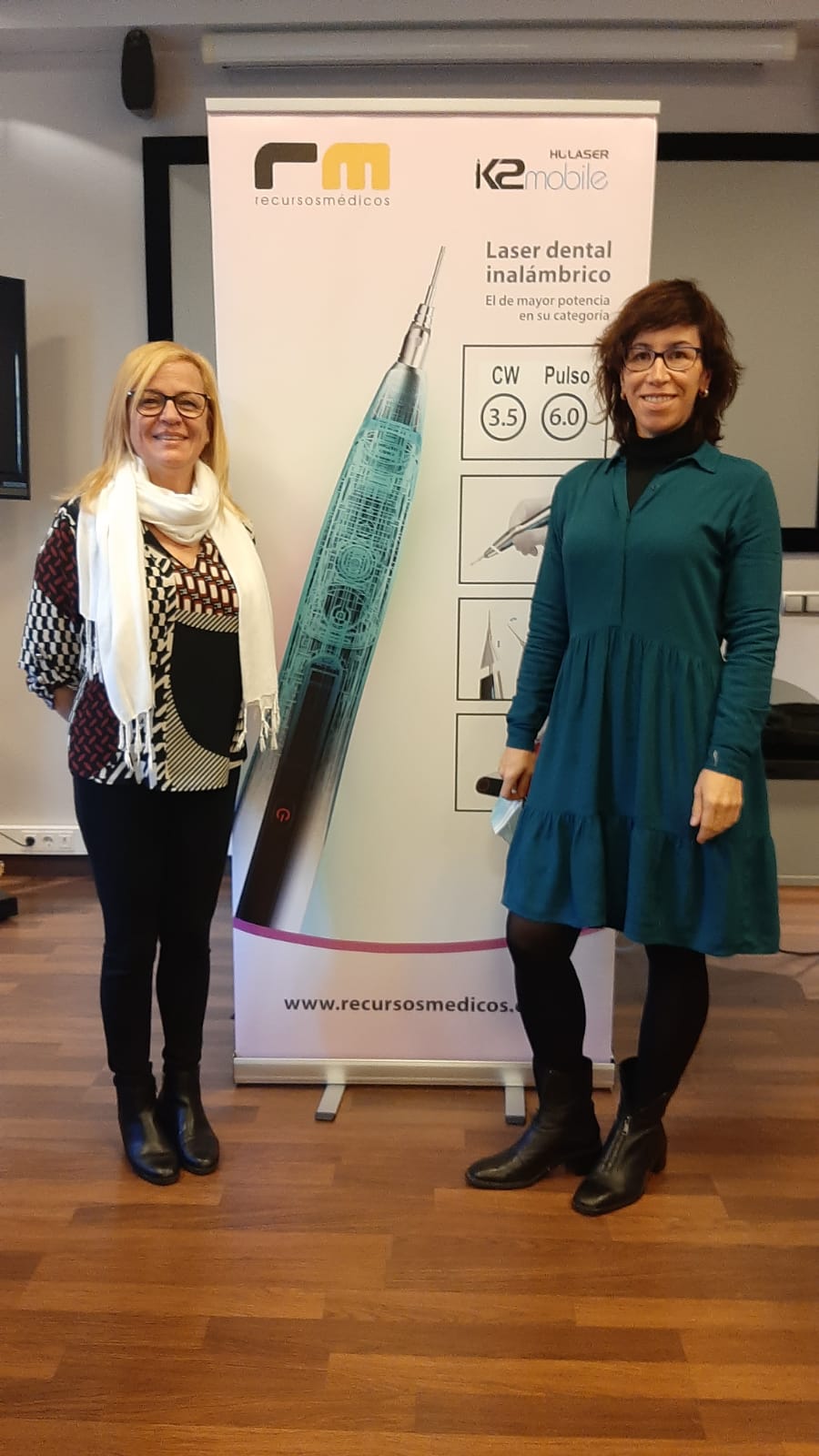
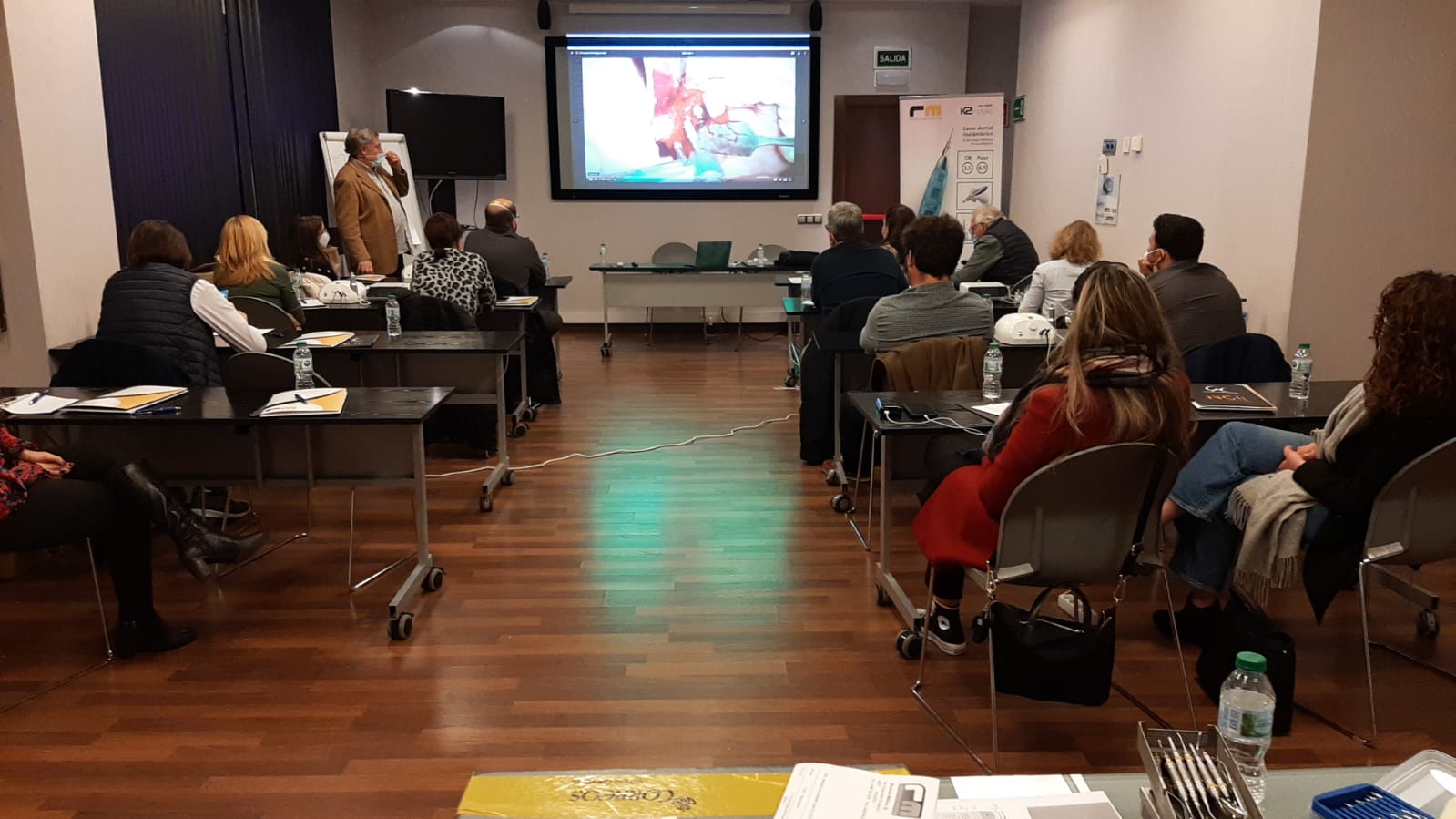
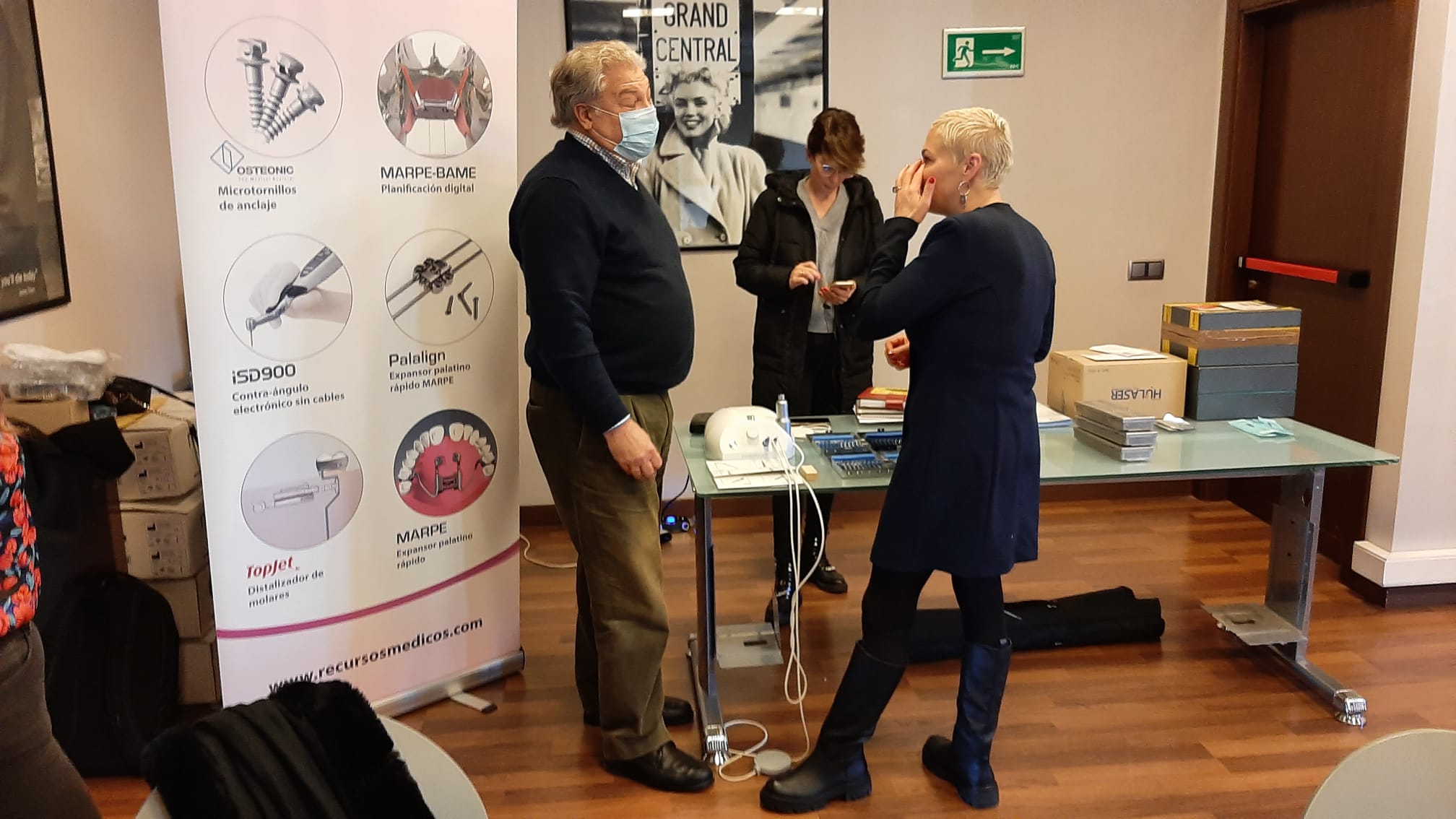
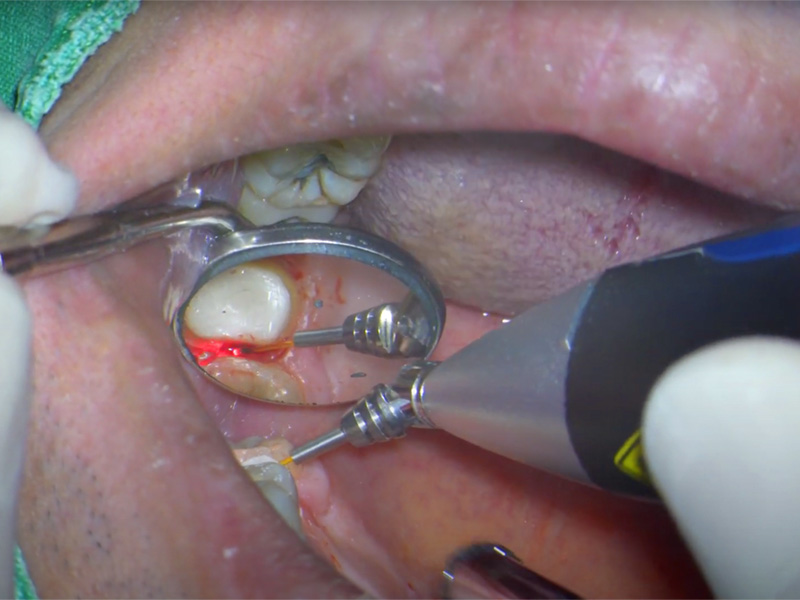
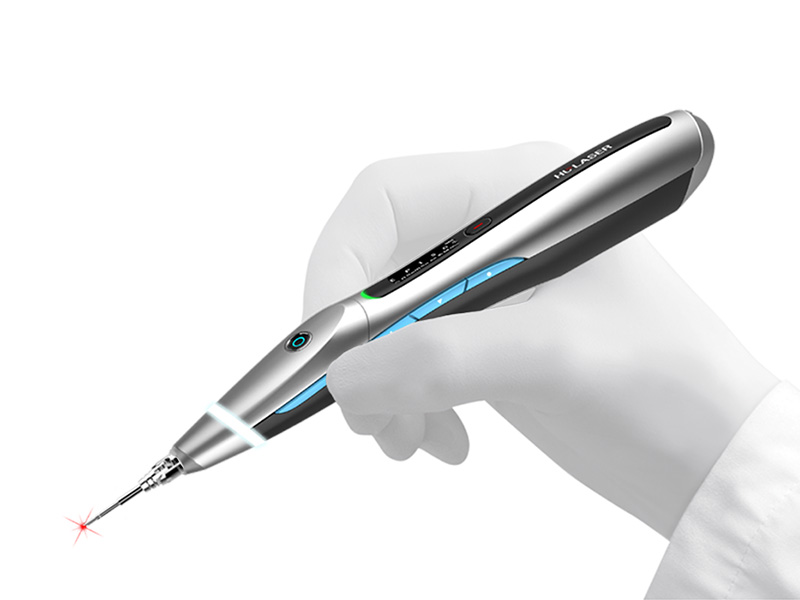
Láser de Diodo. Teórico-Práctico. 25 Marzo 2023.
Aplicaciones en Odontología
-Láser de diodo
Dr. Fernando Gómez-Ferrer Bolinches
Fecha: Sábado, 25 Marzo 2023
de 9:30 a 18:00 horas
Modalidad:
Teórico-Práctico. Presencial.
Cupo: Limitado
Lugar: Hotel Clement Barajas
Av. General, 43
28042 Madrid
Consultas Teléfono 96.342.0478
Descripción y objetivos:
Dirigido a profesionales de la odontología que estando en posesión de las habilidades y conocimientos implantológicos convencionales deseen ampliar sus competencias con una actualización en tecnología avanzada
Objetivos Láser de diodo
Teoría y práctica:
-Presentación
-Comprensión láser de diodo
-Ventajas y utilidades
-Funcionamiento de láser diodo K2 mobile
-Función en perio
-Endodoncia
-Ortodoncia
-Cirugía y láser, implantes
-Aftas, llagas, vestibuloplastias, mucositis
-Fotobioestimulación
-Cirugía sin anestesia
-Taller
-Ruegos y preguntas
Te puede interesar...
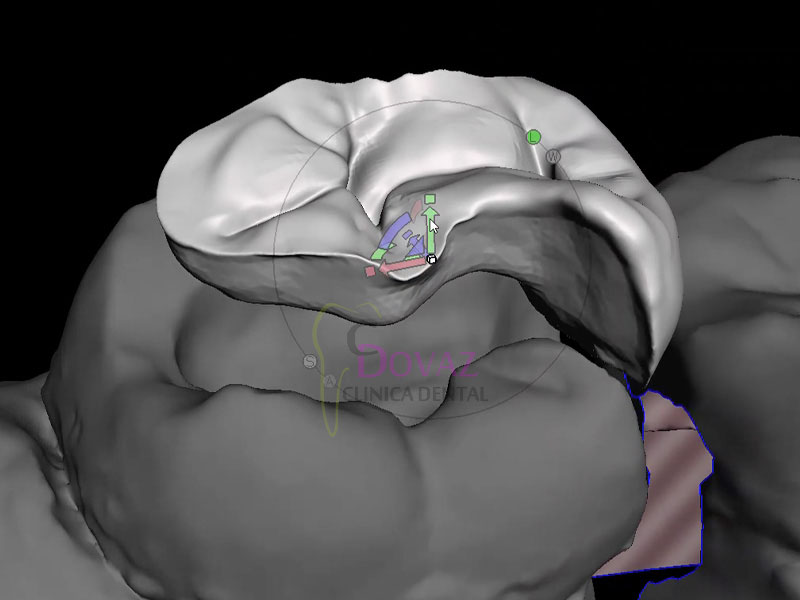
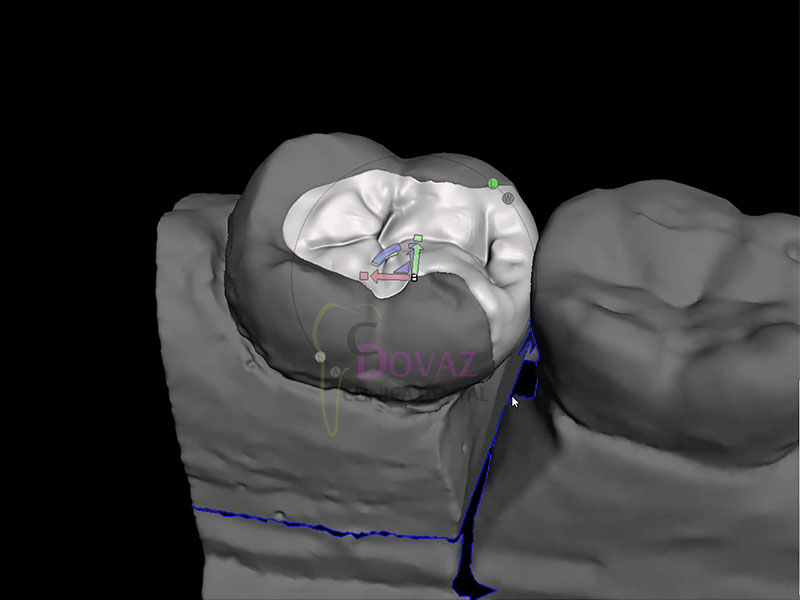
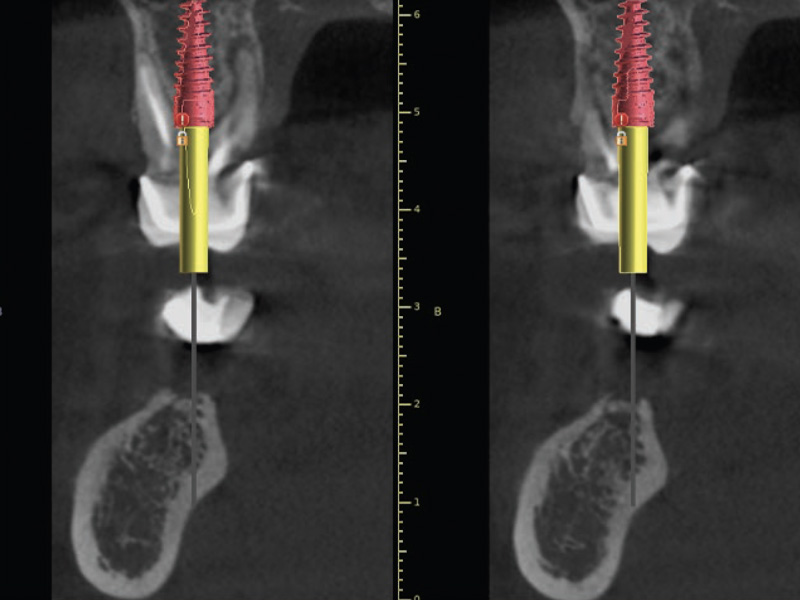
Cirugía Guiada e Impresión 3D. Barcelona. 3-4 Marzo 2023.
Cirugía Guiada e Impresión 3D
Dr. Tal Grauer
Dr. Justo M. Balaguer
Fecha:
3 y 4 Marzo 2023
9:00 a 19:00 horas
Modalidad:
Teórico-Práctico. Presencial.
Cupo: Limitado
Lugar:
Sala Meet & Go
Calle Caballero 72, Local
08029 Barcelona
Consultas Teléfono 96.342.0478
Se entregarán 6 exportaciones BlueSkyPlan gratis a cada asistente
Dirigido a:
Odontólogos y/o estomatólogos que quieran incorporar a su práctica clínica la cirugía implantológica guiada y la impresión 3D.
Uso de software gratuito y compatible con cualquier marca de implantes de elección del facultativo.
Objetivo:
Curso teórico-práctico de planificación digital e impresión 3D para la colocación precisa de implantes mediante cirugía guiada.
La información presentada es aplicable a cualquier sistema de implantes y prácticamente a la totalidad de situaciones clínicas.
El profesional aprenderá el paso a paso del flujo digital con BlueSkyPlan y los procedimientos de impresión 3D.
Programa:
CIRUGÍA GUIADA Y MESHMIXER
– Introducción a la odontología digital y cirugía guiada.
– Requisitos y ventajas.
– Tipos de cirugia guiada y de férulas quirúrgicas.
– Posibles fuentes de error.
– Kits de cirugía guiada disponibles en el mercado.
– Aspectos relevantes.
– Aplicación de software open source (BlueSkyPlan y Meshmixer).
HAND ON 1: Meshmixer
– Herramientas básicas
– Cierre de mallas
– Zocalado y ahuecado de modelos
– Instalación de librerías de dientes
– Encerados diagnósticos. Uso de Overlay2. Confección de provisionales
– Extracciones virtuales y mirroring
– Pilares customizados
CIRUGÍA GUIADA Y BLUESKYPLAN
– Férulas dentosoportadas: Flujos de trabajo digital en BSP
HANDS ON 2: Pacientes parcialmente desdentados
– Implantes unitarios
– Puente sobre implantes
– Implante inmediato
– Férulas mucosoportadas y óseosoportadas: Flujos de trabajo digital en BSP
HANDS ON 3: Pacientes totalmente desdentados
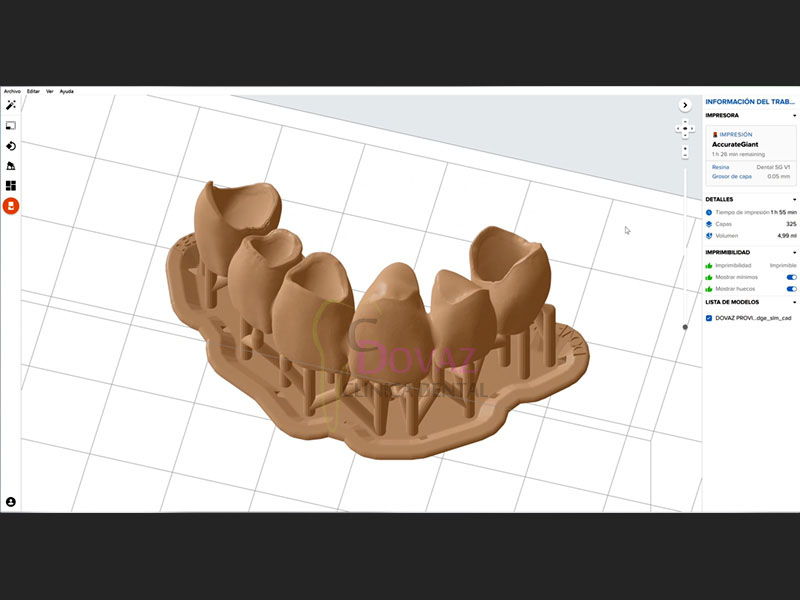
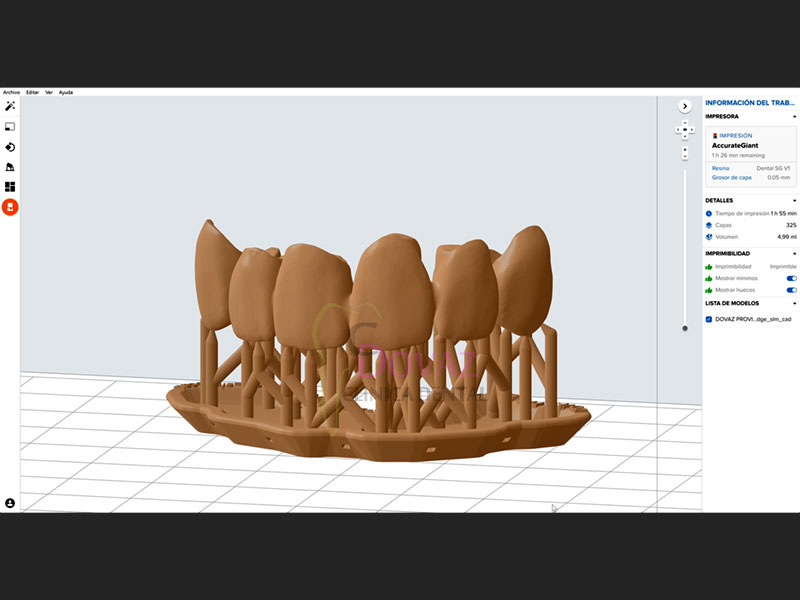
IMPRESIÓN 3D
– Conceptos básicos
– Tipos de impresoras 3D
– Impresoras dentales vs. impresoras genéricas
– Resolución XY y resolución Z
– Implementación de la impresión 3D en la clínica dental
– Procedimientos en impresión 3D
– Tipos de resinas: Principales marcas y aplicaciones
– Coste de la impresión
HANDS ON 4: Impresión 3D
– Partes de la impresora 3D y calibración eje Z
– Calibración de resinas
– Utilización del slicer
– Impresión de modelos y férulas
– Postprocesado
Material imprescindible:
Ordenador con procesador i7 o superior
Sistema operativo Windows 64bits
Memoria RAM 16 GB o superior
Tarjeta gráfica dedicada
Ratón 3 botones
Software: descarga de los sitios web:
Archivos de práctica: se aportan durante el curso
Te puede interesar...
BlueSkyPlan software para planificación
135,00 € – 3.500,00 € + IVANeo NaviGuide, cirugía guiada
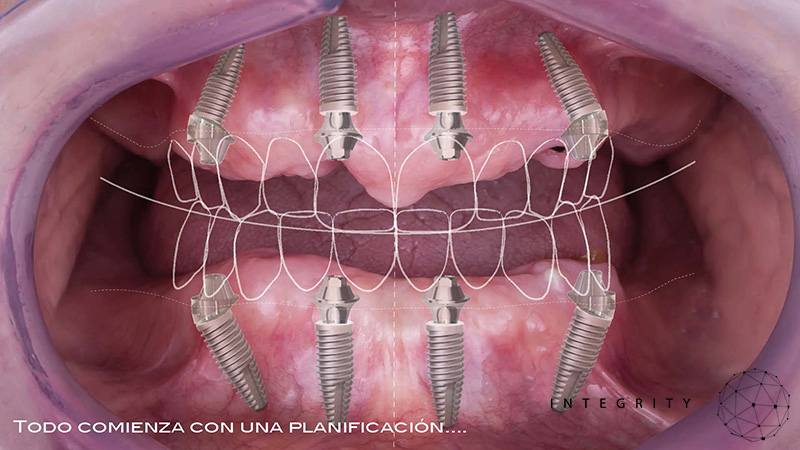
2.800,00 € + IVACarga Inmediata. Integrity. 3 Marzo 2023.
Carga Inmediata
Dr. Jesús Ostos
Dr. Edgar Cabrera
Fecha:
Viernes 3 de Marzo de 2023
10:00 a 20:00 horas
Modalidad:
Teórico-Práctico. Presencial.
Cirugía en directo
Cupo: Limitado
Lugar:
Paseo de Europa, 12 Local 2
28703 San Sebastián de los Reyes
Madrid
Consultas Teléfono 96.342.0478
Descripción:
Dirigido a profesionales de la odontología que estando en posesión de las habilidades y conocimientos implantológicos convencionales deseen ampliar sus competencias con una actualización en la sistematización y de las técnicas de CARGA INMEDIATA
Objetivos:
El objetivo de esta jornada de formación es el abordaje desde un punto de vista práctico de las principales puntos relacionadas con la carga inmediata en rehabilitaciones del maxilar superior e inferior desde el punto de vista quirúrgico y protésico.
-Biología en tratamientos con Implantes Dentales
-Planificación Prótesicamente guiada
-Patrones actualizados de reabsorción ósea. Evaluación Diagnóstica 3D
-Fenómeno de Oseointegración Vs. Cicatrización ósea
-Selección e Identificación de distintos biomateriales disponibles para R.O.G
-Protocolo de manejo de injertos en zona mandibular anterior
-Protocolo de manejo de injertos de tejido blando
-CUÁNDO-CÓMO-DÓNDE
-Manejo del sitio de extracción inmediato, temprano o tardío
-Discusión de Casos Clínicos
PROGRAMA
Programa:
10:00 – 14: 00 horas Teoría
-Tiempos de carga.
-Implantes postexodoncia. Diseños de implantes para carga inmediata
-Carga inmediata unitaria y parcial en sector anterior
-Carga inmediata para rehabilitaciones completas
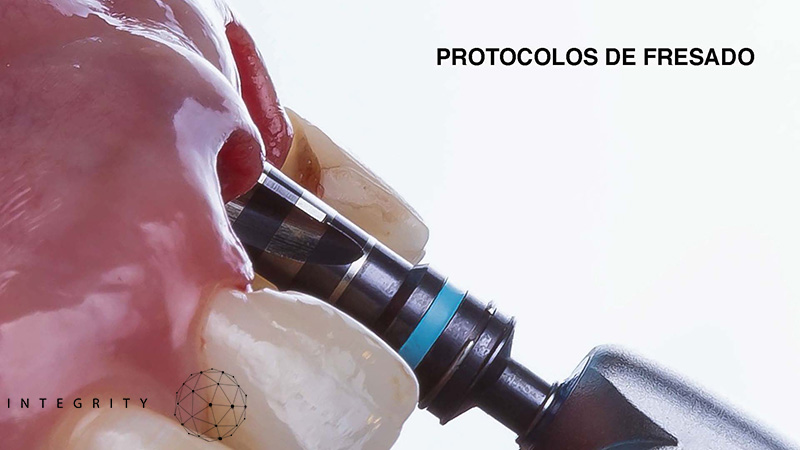
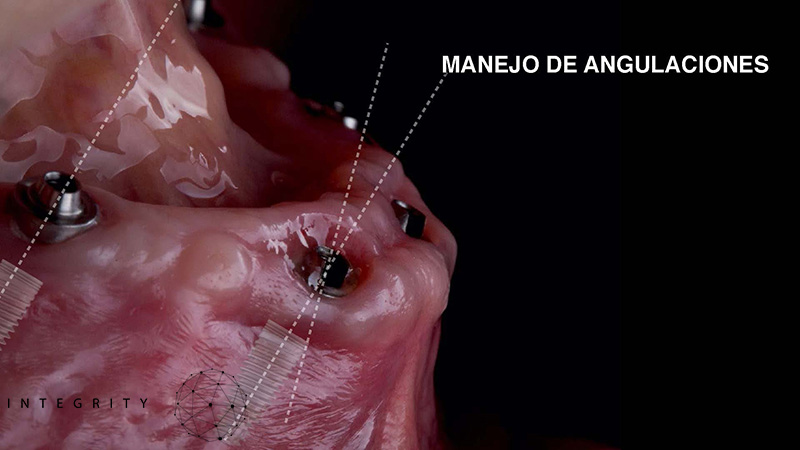
-Consideraciones protésicas: manejo de las angulaciones.
-Selección de componentes protésicos
-Principios de cirugía: manejo de tejidos blandos, orientación de implantes en los tres planos del espacio.
-Valoraciones Anatómicas.
-Anatomía quirúrgica. Seno maxilar y nervio dentario inferior.
-Complicaciones.
14:00 – 16:00 horas
-Comida
16:00 – 20:00 horas Cirugías en Directo
–Cirugía en directo. Paciente de carga inmediata de maxilar completo.
-Colocación de implantes y selección de aditamentos protésicos
-Confección de provisionales para carga inmediata
-Colocación de la prótesis provisional inmediata




Te puede interesar...
Implante cónico IS-II active, hexágono interno
Inicia sesión o solicita tu usuario para ver el precioVIII Congreso Internacional de Alineadores (Alignea). 9 al 11 Febrero 2023.
VIII Congreso Internacional de Alineadores (Alignea). 9 al 11 de Febrero de 2023.

Gracias Dra Jingting Lu for la fantástica conferencia
“A new orthopedic approach using clear appliances S8-SGTB and S8-SGHB to correct severe jaw discrepancies”
9 de Febrero 2023
15:00 horas
Dr. Jingting Lu MD, Ph.D,
-Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine Senior Ortho Expert
-Dean of Shanghai Lujingting Dental Clinic
-Director of Department of Orthodontics, Dingzhi Dental
-Member of Shanghai Stomatological Association
-Member of Chinese Academy of Esthetic Dentistry
Fecha: 9 al 11 de Febrero de 2023
Lugar:
Palacio de Congresos de Ávila.

VIII Congreso Internacional de Alineadores.
Programa

Mira productos asociados...
No lo encontramos.